10 Best Drones for Mapping in 2026 (A Complete Buying Guide)
Drones have completely changed the game in modern mapping, making data collection incredibly efficient and precise. With their advanced sensors and high-res cameras, they're giving mapping experts like you the power to capture detailed geospatial data with ease. This tech not only speeds up mapping but also helps you tackle tough terrains and emergency situations. From urban planning to agriculture, their applications are diverse.
Now, here's the kicker: choosing the right drone is crucial for nailing data collection. You've got to consider stuff like flight time, payload capacity, camera specs, and software compatibility. These factors have a direct impact on the quality of your data.
In this article, we'll dive into how drones are used in mapping, what features to look out for when picking one, why advanced sensors matter, and even compare different types of mapping drones.

10 Best Drones for Mapping and Surveying
We conducted rigorous testing on 10 of the most popular mapping drones available in the market today. These drones were put through their paces, and we've compiled the essential data, along with their advantages and disadvantages, to help you make the right choice for your specific mapping requirements.
WingtraOne Gen II | Sensefly eBee X | DJI Matrice 350 RTK | Freefly Alta X with RTK | DJI Phantom 4 RTK | Autel EVO II Dual 640T Enterprise | Yuneec H520 RTK | DJI Mavic 3 Enterprise | |||
Platform type | Redundant VTOL | Redundant VTOL | Tailsitter VTOL | Fixed wing | Quadcopter | Quadcopter | Quadcopter | Quadcopter | Hexacopter | Quadcopter |
Max. flight time | 180min | 90min | 59mins | 60/90min | 55min | 50min | 30min | 42min | 30min | 45min |
Coverage at 3cm/px | 700HA | 600HA | 400HA | 220HA/500HA | 200HA | 150HA | 100HA | 90HA | 50HA | 50HA |
Control range | 30/50km | 35km | 10km | 3km | 8km | 1.5km | 7km | 15km | 1.6km | 15km |
Max. resolution | 61MP | 61MP | 61MP | 24MP | 45MP | 50/100MP | 20MP | 50MP | 20MP | 12 MP |
PPK & RTK | PPK & RTK | PPK & RTK | PPK | PPK & RTK | RTK | RTK | RTK | RTK | RTK | RTK |
Payload capacity | 3kg | 1kg | 0.8kg | 1.6kg | 2.7kg | 16kg | 1.5kg | 1kg | 1.6kg | 0.9kg |
Obstacle avoidance | Yes | Yes | No | No | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
JOUAV CW-15: Best LiDAR Drone for Large Area Mapping
The JOUAV CW-15 stands out as a top-tier LiDAR drone designed for large-area mapping tasks. The JoLiDAR-120 offers impressive specs such as a 1430-meter measuring range, 1.8 million points/second maximum point frequency, and 15 maximum echo counts. This ensures unmatched vertical and horizontal accuracy, with precision better than 3cm and 5cm, respectively.
One of the standout features of the CW-15 is its advanced point cloud processing software, which enhances data accuracy through automatic matching, segmentation, leveling, and more. This drone can vertically take off and land even in confined spaces like cliffs and forests, providing excellent adaptability.
With a maximum flight time of 180 minutes, it ensures extended missions and its RTK and PPK capabilities offer centimeter-level autonomous vertical landing and high-precision POS data. Furthermore, it can autonomously avoid obstacles, adapt to various terrains, and detect other drones equipped with ADS-B modules. With a payload capacity of 3 kg and an open architecture for customization, the CW-15 is suitable for professionals in fields like surveying, infrastructure inspection, security surveillance, and agriculture.
Pros:
- Cutting-edge LiDAR technology with impressive specifications
- Advanced point cloud processing software for enhanced data accuracy
- Versatile applications in surveying, infrastructure inspection, security surveillance, and agriculture
- VTOL capability for confined space operations
- Long flight time, high-speed cruising, and extended control range
- Modular payload and open architecture for user-defined load application development
- Autonomous obstacle avoidance and terrain adaptability
- Durable carbon fiber airframe for stability and durability in various conditions
Cons:
- High-end features come with a corresponding investment
- May require training to fully leverage advanced functionalities
JOUAV CW-007: Best VTOL Drone for GIS Mapping
The JOUAV CW-007 is a versatile VTOL (Vertical Take-Off and Landing) drone tailored for GIS mapping tasks. With its CA103 61MP full-frame RGB camera featuring an illuminated CMOS sensor and 35mm lens, this drone offers exceptional image quality and accuracy, making it an ideal choice for professionals in surveying, infrastructure inspection, security surveillance, and agriculture. Achieving an absolute accuracy of down to 1cm, it excels in delivering precise mapping data.
With high efficiency, the CW-007 can cover large areas in a single flight, making it a highly productive tool for mapping. Its modular design allows for easy setup and takedown in under 2 minutes without the need for tools.
The drone also features autonomous flight capabilities, enabling it to automatically avoid obstacles during flight and return autonomously in case of issues. Built with a robust carbon fiber airframe, it ensures stability and durability even in challenging conditions, including light rain and snow.
Pros:
- High-resolution imaging with the CA103 61MP full-frame RGB camera
- Exceptional absolute accuracy down to 1cm
- Versatile applications in surveying, infrastructure inspection, security surveillance, and agriculture
- VTOL capability for operations in confined spaces
- Efficient mapping capabilities covering large areas in a single flight
- Quick and tool-less setup with a modular design
- Autonomous obstacle avoidance and autonomous return functions
- Robust carbon fiber airframe for durability and stability in various conditions
Cons:
- Comes at a higher price compared to some alternatives
- Lacks a LiDAR sensor, which may limit suitability for certain applications
WingtraOne Gen II: Best Drone for Photogrammetry
The WingtraOne Gen II stands out as an exceptional drone for photogrammetry and mapping tasks. Equipped with a Sony 61MP RGB camera, it excels in capturing high-resolution images for precise mapping. It's ideal for surveying, precision agriculture, and infrastructure inspection.
With a Tailsitter VTOL platform, it offers a remarkable flight time of up to 59 minutes, covering extensive areas in a single flight. The drone boasts a control range of 10 kilometers and supports PPK (Post-Processed Kinematic) for accurate georeferencing without ground control points. Additionally, it can carry specialized cameras like the Sony a6100 Oblique camera for 3D modeling and multispectral sensors for agriculture.
Pros:
- High-quality Sony 61MP camera
- Versatile applications in surveying and agriculture
- Long flight time and impressive control range
- PPK technology eliminates the need for ground control points
- Capable of carrying various specialized cameras
- Small learning curve for operators
Cons:
- Limited payload capacity (0.8 kilograms)
- Lack of obstacle avoidance features
- Not suitable for adverse weather conditions
- Inability to carry LiDAR or thermal sensors
- Primarily designed for mapping, limiting versatility
- Increased susceptibility to tipping due to wing-tip rotors
- Glass fiber airframe is heavier and less durable than carbon fiber
eBee X: Best Fixed-Wing Drone for Mapping
For those seeking a fixed-wing drone for mapping, the eBee X is a top choice. Its unique Endurance Extension offers an impressive flight time of up to 90 minutes, allowing for extensive coverage of large areas without the need for frequent landings. With High-Precision on Demand, it achieves remarkable accuracy, down to 3 cm, without the requirement of ground control points.
This drone is lightweight, weighing just 700g, making it easy to transport. It's suitable for surveying, precision agriculture, and infrastructure inspection. The eBee X can also carry specialized cameras for 3D reconstructions and thermal mapping, making it a versatile option for mapping professionals.
Pros:
- Exceptional flight time of up to 90 minutes
- High accuracy without the need for ground control points
- Lightweight and easy to transport
- Available with RTK and PPK for positional accuracy
- Compatible with various specialized cameras
- Advanced flight mission planning software (eMotion)
- Simulator mode for training and optimization
Cons:
- Limited control range.
- Not recommended for adverse weather conditions
- Lacks a LiDAR sensor
- Foam body build may limit durability and payload capacity
- Low-resolution camera
- Requires planning for a safe landing area
- Hand launch can be risky without experience
DJI Matrice 350 RTK: Best RTK Drone for Mapping
The DJI Matrice 350 RTK is a formidable multirotor drone that excels not only in inspection and search and rescue missions but also in various mapping applications. Equipped with the latest RTK technology, this drone offers unparalleled precision and navigation capabilities, even in challenging environments. With an impressive 55 minutes of flight time, it can cover substantial areas in a single flight.
The Matrice 350 RTK's rugged construction ensures it can withstand tough conditions, making it suitable for a range of mapping tasks. Its triple-redundant system and advanced navigation technology guarantee accuracy and reliability. Additionally, this RTK drone features a high-performance gimbal system for stable imaging during flight and offers real-time, in-flight camera control. LiDAR compatibility further enhances its mapping capabilities.
Pros:
- Precise RTK technology for accurate mapping
- Extended 55-minute flight time
- Rugged construction is suitable for tough conditions
- High-performance gimbal system for stable imaging
- Advanced obstacle detection sensors for safe flying
- Real-time camera control and LiDAR compatibility
Cons:
- Limited flight time when carrying heavy payloads
- Complex propeller replacement process
- Large batteries require frequent changes
- Limited elevation data options in the software
- Massive batteries for longer missions
Freefly Alta X with RTK: Best Drone for 3D Mapping and Modelling
The Freefly Alta X with RTK is an excellent choice for 3D mapping and modeling applications. This drone stands out for its modular design, allowing for easy integration of various payload systems, and making it adaptable for a wide range of mission requirements.
With four powerful motors capable of 100A Max continuous power output, the Alta X can carry payloads weighing up to 16kg. It boasts an impressive 50-minute flight time and a top speed of 137km/h, making it suitable for dynamic mapping tasks. The drone is compatible with a range of payloads, including gimbaled IR, mapping cameras, LiDAR, hyperspectral sensors, and delivery systems. Its advanced blade design reduces vibrations, ensuring cleaner data collection and high-quality footage.
Pros:
- Modular design for versatile payload integration
- High payload capacity of up to 16kg
- Impressive 50-minute flight time
- Compatibility with various sensors and cameras
- Advanced blade design for reduced vibration
- RTK and PPK mapping camera support
Cons:
- Heavy build, weighing 76.9 pounds
- Limited flight range of 1.5km
- Reduced flight time with payloads onboard
- Lack of obstacle avoidance features
DJI Phantom 4 RTK: Best Entry-level Drone for 3D Mapping
The DJI Phantom 4 RTK stands out as an excellent entry-level option for those looking to dive into the world of mapping. It boasts several remarkable features that enhance its mapping capabilities. With its integrated RTK module, the Phantom 4 RTK provides real-time centimeter-level positioning data, improving the absolute accuracy of image metadata. This ensures precise mapping results, making it ideal for surveyors and GIS professionals.
Additionally, its compatibility with 4K and FLIR Vue 336 thermal imaging cameras extends its utility to industrial inspections, search and rescue operations, and more. The drone's user-friendly setup and reliable autopilot system make it accessible for both beginners and experts. Furthermore, its advanced obstacle detection and avoidance system ensures safety during complex mapping missions.
Pros:
- Real-time centimeter-level positioning (RTK)
- Compatibility with 4K and thermal imaging cameras
- User-friendly setup for all skill levels
- Reliable autopilot system
- Advanced obstacle detection and avoidance
- Affordable price for the features offered
Cons:
- Limited flight time (30 minutes)
- Payload capacity limited to 1.5kg
- Lower camera resolution (1-inch CMOS 20MP)
- No LiDAR capability
Autel EVO II Dual 640T Enterprise: Best Drone for Thermal Mapping
When it comes to thermal mapping, the Autel EVO II Dual 640T Enterprise is a standout choice. This drone offers a remarkable 15km video transmission range and impressive 8-level wind resistance, ensuring it can tackle challenging mapping tasks. With dual cameras that support infrared thermal imaging at a resolution of up to 640x512@30 fps, the EVO II Dual 640T excels in capturing detailed thermal data.
Additionally, it features an 8K video camera, 4K HDR video, a 48MP camera, and 4x lossless zoom for high-definition aerial views. Intelligent route planning, obstacle avoidance, and AI algorithms further enhance its mapping capabilities. The Autel VIO positioning feature ensures safe returns even in adverse conditions, and the RTK module offers centimeter-level accuracy. With 19 sets of sensors, including vision sensors and dual IMU, this drone can easily create 3D maps and real-time terrain data.
Pros:
- Impressive video transmission range and wind resistance
- Dual cameras for infrared thermal imaging
- High-resolution cameras for detailed data
- Intelligent route planning and obstacle avoidance
- Precise positioning with Autel RTK module
- Versatile sensors for 3D mapping
Cons:
- Limited flight time (42 minutes)
- Lower coverage efficiency
- Payload capacity limited to 1kg
- Lack of live spot metering and temperature alerts
- No LiDAR capability
Yuneec H520 RTK: Cheapest Drone for Mapping
Yuneec's H520 RTK is a budget-friendly mapping powerhouse that combines affordability with essential features for precise aerial mapping. It comes equipped with GPS and GLONASS for highly accurate positioning, making it a reliable choice for various applications.
This six-rotor hexacopter boasts retractable landing gear, enhancing its stability during flight. What sets the H520 RTK apart is its interchangeable gimbal system, allowing you to use one of three hot-swappable options. The gimbal features 360-degree continuous rotation and a 7-inch display on the controller, ensuring you have a clear view of your mapping data.
Pros:
- GPS and GLONASS for accurate positioning
- Interchangeable gimbal system with 360-degree rotation
- Precision compass for flying in challenging environments
- A budget-friendly option for entry-level mapping
- Retractable landing gear for added stability
Cons:
- Low-resolution 20MP camera
- A short transmission range (1.5km) may limit coverage
- Brief flight time (30 minutes) with each battery
- Lack of autonomous flight modes
DJI Mavic 3 Enterprise: Best DJI Drone for Mapping
For those seeking top-tier mapping capabilities, the DJI Mavic 3 Enterprise stands out as the best DJI drone for mapping purposes. It's equipped with a state-of-the-art hybrid zoom camera offering up to 56x zoom and a mechanical shutter to prevent motion blur during high-speed surveys.
This drone can be further enhanced with an optional RTK module, providing centimeter-level accuracy. With a remarkable 15 km maximum control range, the Mavic 3 Enterprise excels at long-distance flights and maintains a stable signal even at maximum distances. Its DJI AirSense system ensures safety by warning pilots of nearby aircraft, enhancing overall security during missions.
Pros:
- High-resolution zoom camera with mechanical shutter
- Optional RTK module for centimeter-level accuracy
- Long control range (15 km) for extended coverage
- DJI AirSense system for enhanced safety
- Thermal camera support with advanced zoom features
- Omnidirectional obstacle avoidance for added security
Cons:
- Lower-resolution 20MP sensor compared to some competitors
- Limited ability to carry survey-quality lidar sensors
- The higher price point for professional-grade mapping
What are the Benefits of Drone Mapping?
Drone mapping offers a multitude of advantages, from cost-effective real estate assessments to enhancing agricultural practices. Discover the extensive benefits that come with integrating drones into your mapping endeavors.
High Precision and Accuracy
One of the most compelling benefits of using drones for mapping is their ability to provide high precision and accuracy in data collection. Aerial mapping drones, such as CW-007 and CW-15, are equipped with advanced GPS and GNSS systems, allowing them to capture data with centimeter-level accuracy. This level of precision is invaluable in fields like surveying, GIS mapping, and construction, where even minor inaccuracies can lead to costly errors.
Cost-Effective Data Collection
Traditional methods of data collection, such as manual surveys or manned aerial photography, are not only time-consuming but also expensive. Drones offer a cost-effective alternative. They require minimal manpower, and the operational costs are significantly lower. As a result, businesses and organizations can collect valuable mapping data without breaking the bank.
Efficient and Rapid Data Collection
Drones excel in covering vast areas quickly and efficiently. Whether you need to survey a construction site, monitor agricultural fields, or map a large real estate property, drones can accomplish the task in a fraction of the time it would take using traditional methods. This efficiency translates to quicker project timelines and faster decision-making.
Enhanced Safety
In industries like construction, where safety is paramount, drones have made a remarkable impact. They can access hard-to-reach or hazardous areas without exposing humans to risks. For example, drones can inspect construction sites, bridges, or mining operations, reducing the need for workers to perform dangerous tasks.
Versatility in Applications
Drone mapping isn't limited to a specific industry; it's incredibly versatile. Aerial mapping drones can be customized with various sensors and cameras to suit specific applications. Whether you need thermal imaging for agriculture, lidar scanning for topographic surveys, or high-resolution cameras for real estate marketing, there's a drone configuration to meet your needs.
What is Drone Mapping Used for?
Drone mapping has diverse applications, including real estate, mining, security, agriculture, and emergency response like fire investigation. Explore how drones are revolutionizing each of these sectors.
Real Estate
In the realm of real estate, the utilization of mapping drones has become indispensable. Realtors, property developers, and land surveyors have embraced these aerial mapping drones for several reasons. Firstly, drones provide breathtaking aerial views of properties, enhancing the marketing of real estate listings. Potential buyers can now explore properties from the comfort of their screens, thanks to high-resolution cameras mounted on drones.
Additionally, mapping drones aid in land surveying, accurately measuring boundaries, and identifying potential issues such as encroachments. This technology expedites the due diligence process and reduces the risk of disputes.

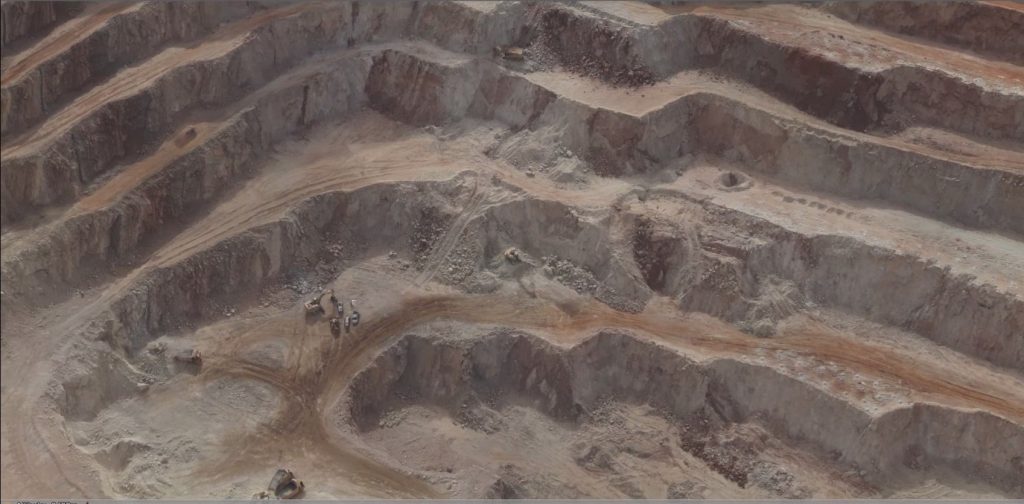
Mining and Metals
Mining drones have been increasingly used by companies to improve efficiency and safety in their operations. They can survey vast mining sites, providing highly detailed, up-to-date maps and 3D models. This data aids in mine planning, ensuring optimal resource extraction while minimizing environmental impact.
Drones equipped with LiDAR technology can penetrate vegetation and dust, revealing the terrain beneath, even in challenging conditions. The real-time data gathered by these drones helps in monitoring stockpiles, ensuring accurate inventory management.

Security and Surveillance
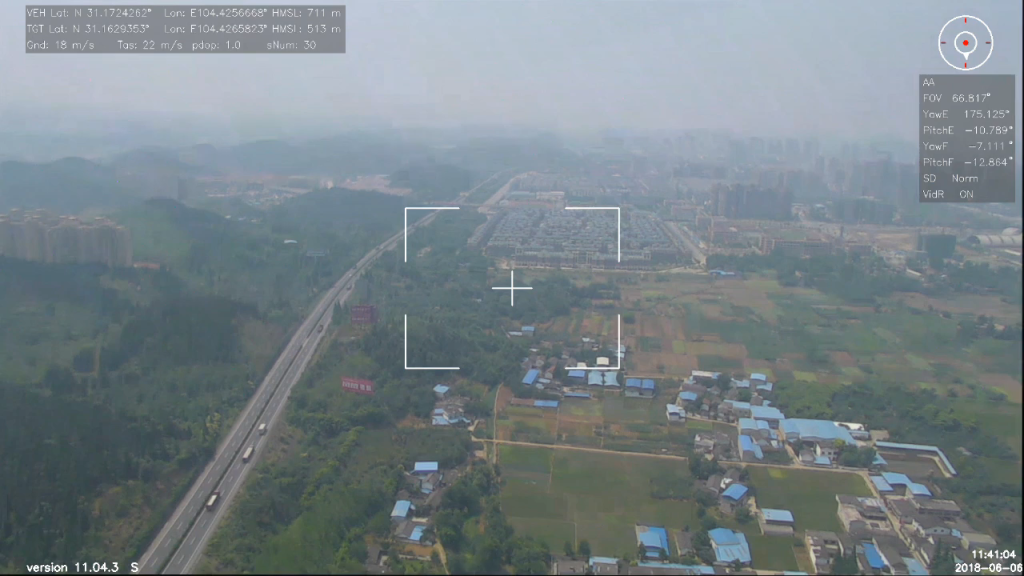
Security professionals are harnessing the power of mapping drones for comprehensive surveillance and monitoring. Drones equipped with advanced cameras and thermal imaging capabilities can patrol large areas efficiently. In critical infrastructure protection, these drones can detect unauthorized access, potential threats, and perimeter breaches.
They are also valuable in disaster management, providing a bird's-eye view during emergencies and natural disasters. Surveillance Drones empower security teams with real-time data, allowing swift decision-making and response.

Agriculture
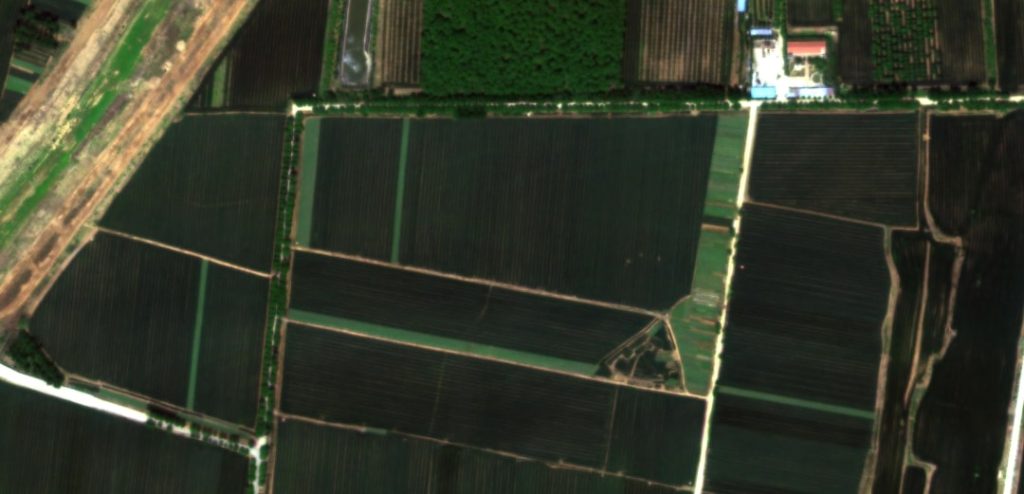
The agricultural sector has embraced drone technology to usher in a new era of precision farming. Agricultural drones equipped with multispectral and thermal cameras are used for crop monitoring and management. They can capture valuable data on plant health, pest infestations, and irrigation needs.
With this information, farmers can optimize resource allocation, reduce chemical usage, and ultimately increase crop yields. Drones are particularly beneficial for large farms, where manually inspecting vast fields can be time-consuming and labor-intensive.

Emergency Response
In times of crisis, drone mapping plays a pivotal role in emergency response, particularly in fire investigation. Mapping drones can access areas that are hazardous or difficult for humans to reach. Equipped with thermal cameras, they can quickly identify hotspots and areas of concern during wildfires.
This real-time information guides firefighting efforts, ensuring that resources are deployed effectively. Additionally, drones help investigators reconstruct fire scenes, aiding in post-incident analysis and insurance claims.
What to Consider When Choosing a Drone for Mapping?
Selecting the perfect mapping drone involves considering various factors. We'll guide you through making an informed choice based on:
Types of Drones
The first decision to make is whether you need a fixed-wing or a multi-rotor drone.
- Fixed-Wing Drones: These are ideal for large-area mapping tasks. They can cover substantial ground and typically have longer flight times compared to multi-rotor drones. If you're mapping extensive agricultural fields or conducting surveys over large construction sites, a fixed-wing drone might be the best choice.
- Multi-Rotor Drones: Multi-rotor drones, like quadcopters and hexacopters, are versatile and can hover in place. They are suitable for more precise and detailed mapping in smaller areas. If you need to capture fine-grained data for real estate mapping or 3D modeling, a multi-rotor drone is a solid option.
- Hybrid VTOL Drones: Hybrid VTOL drones combine the benefits of both fixed-wing and multi-rotor designs. They can take off and land vertically like a multi-rotor drone but also transition to fixed-wing flight for greater endurance and coverage. Hybrid VTOL drones are excellent for applications where flexibility and efficiency are crucial, such as long-range mapping missions with the ability to cover large areas and land in confined spaces.

Camera Quality and Payload Capacity
The quality of your mapping data depends heavily on the drone's camera capabilities. Here's what to consider:
- Resolution: Look for drones with high-resolution cameras (e.g., 20MP or more) to capture detailed images. This is essential for producing accurate maps and 3D models.
- Zoom and Thermal Capabilities: Some mapping drones come with zoom and thermal imaging cameras. These are valuable for tasks like wildlife tracking, search and rescue, and thermal mapping.
- Payload Capacity: If you need to attach additional sensors, such as LiDAR or multispectral cameras, ensure that the drone has the necessary payload capacity.

Flight Time and Range
Consider the drone's flight time and control range. Longer flight times are advantageous for covering larger areas without frequent battery swaps, while extended control ranges allow you to operate the drone from a safe distance. Look for options with at least 30 minutes of flight time and a control range of several kilometers for versatility.
RTK and GPS Accuracy
For precision mapping and surveying, drones equipped with Real-Time Kinematic (RTK) and GPS are invaluable. RTK technology provides centimeter-level accuracy, ensuring your mapping data is highly reliable. This feature is particularly important for applications like agriculture and construction, where precision is paramount.
Ease of Use and Autonomy
Consider your level of expertise when choosing a mapping drone. Some models offer autonomous flight modes and obstacle avoidance systems, making them suitable for beginners. Advanced users may prefer drones that allow manual control for greater flexibility.
Software and Data Processing
Mapping drones are only part of the equation. You'll also need robust software for data processing and analysis. Ensure that the drone you choose is compatible with popular mapping and GIS software packages.
Specific Industry Requirements
Tailor your drone selection to the specific needs of your industry:
- Agriculture: Consider drones with multispectral cameras for crop health analysis.
- Construction: Look for construction drones with high-resolution cameras for site surveys and progress tracking.
- Mining: Consider robust drones capable of operating in harsh environments.
- Real Estate: Focus on drones with good camera quality for property photography and 3D modeling.
How to Use a Drone for Aerial Mapping?
Learn the step-by-step process of using drones for aerial mapping and surveying. From mission planning to data collection, we'll guide you through the entire process.
- Flight Planning: Plan your flight path using specialized mapping software. This ensures systematic coverage of the area of interest and optimal data collection.
- Ground Control Points (GCPs): Place GCPs in the mapping area to enhance accuracy. GCPs are known reference points that help georeference the aerial images.
- Overlap and Altitude: Maintain proper overlap (frontlap and sidelap) between images to avoid data gaps. Adjust the altitude for the desired Ground Sampling Distance (GSD), which impacts image resolution.
- Camera Settings: Configure camera settings, such as shutter speed, ISO, and aperture, for the best image quality. Use manual settings when possible to maintain consistency.
- Data Processing: After the flight, process the collected data using specialized software to create orthomosaics, digital surface models (DSMs), and 3D point clouds.
What Factors Influence Drone Mapping Accuracy?
Achieving accurate drone mapping depends on several factors. Explore how altitude, camera settings, and ground control points influence mapping accuracy and how to optimize them.
Mission Parameters
When embarking on a drone mapping mission, it's essential to carefully consider several mission parameters to achieve the desired level of centimeter (cm) accuracy:
- Image Resolution: The quality of your mapping data starts with the resolution of the images captured by your drone. Higher-resolution imagery results in better data. To attain this, opt for a camera with a high pixel resolution. A minimum of 12 megapixels is required, with 20 megapixels considered ideal for precision mapping.
- Altitude: The altitude at which you fly your drone plays a crucial role in accuracy. Flying higher allows you to cover larger areas quickly but with reduced accuracy. Conversely, flying lower takes more time but significantly improves mapping accuracy. Thus, lower altitudes are preferred for precise mapping tasks.
- Image Overlap: Overlapping of images is another vital parameter. Greater overlap reduces the chances of data gaps caused by camera rotations, tilt, flying height variations, and terrain changes. While more overlap increases flight times, it's a worthwhile trade-off for improved accuracy. Aim for at least 60% side overlap and 75% front overlap, with up to 85% overlap for challenging terrains.
Environmental Conditions
Environmental factors can significantly affect drone mapping accuracy. Here are two critical considerations:
- Weather Conditions: Choose your mapping days wisely. Avoid flying in strong winds, dense cloud formations, or smog whenever possible. While many drones can handle high winds, it's best to steer clear of winds exceeding 7 meters per second (15 mph) for precise mapping.
- Obstacles: In urban environments, tall structures like skyscrapers can obstruct GNSS (Global Navigation Satellite System) signals, leading to multi-path interference and inaccurate data. Be mindful of such "Urban Canyon" scenarios and plan your flights accordingly.
Ground Control Points (GCPs)
Ground control points are indispensable for achieving high mapping accuracy. These reference markers laid out across the mapping area provide known, accurate coordinates on the ground. Here's what you should know:
- Quantity of GCPs: The number of GCPs you use is a subject of study. While more GCPs can significantly enhance mapping accuracy, there's a point of diminishing returns. It's essential to consider the area and terrain. As a general guideline, aim for at least five GCPs on your site.
- Distribution of GCPs: The strategic placement of GCPs matters. Research has shown that evenly distributing GCPs in a triangular mesh grid formation can effectively double their impact on accuracy. Additionally, consider placing GCPs in the corners of the site and at the highest and lowest points for optimal results.
How to Choose the Best Mapping Camera for Drone Photogrammetry?
Selecting the right camera is pivotal for successful drone photogrammetry. Gain insights into how to choose the best mapping camera that aligns with your specific needs and budget.
Camera Sensor Size and Resolution
The first and foremost consideration is the camera's sensor size and resolution. A larger sensor typically captures more detail and offers better performance in challenging lighting conditions. For mapping purposes, look for cameras with sensors in the APS-C or full-frame range. Resolution matters too - opt for cameras with high megapixel counts (typically 20MP or more) to ensure sharp and detailed imagery, which is crucial for precise photogrammetric results.
Lens Quality and Focal Length
The quality of the camera's lens is equally important. A high-quality lens minimizes distortions and aberrations, leading to more accurate mapping. Additionally, consider the focal length of the lens. A fixed wide-angle lens (around 35mm) is often a preferred choice for photogrammetry, as it minimizes distortion and simplifies the image processing workflow. However, some applications may require interchangeable lenses for versatility.
Shutter Type and Speed
The camera's shutter type and speed are vital for capturing sharp images during drone flight. Cameras with mechanical shutters are preferable because they reduce the risk of motion blur. Additionally, choose a camera with fast shutter speeds to capture crisp images, especially when flying at higher speeds or altitudes.
GPS and Geotagging Capability
To streamline the georeferencing process, opt for a camera with built-in GPS or geotagging capability. This feature automatically embeds GPS coordinates in each image's metadata, simplifying the alignment of images during post-processing. Geotagged images save time and ensure precise mapping results.
Compatibility and Integration
Consider the compatibility of the camera with your drone. Some drone manufacturers offer proprietary camera options that seamlessly integrate with their platforms. This integration can simplify operations and ensure optimal performance. Check for third-party cameras that are compatible with your drone if you prefer more flexibility.
Post-Processing Workflow
Take into account the camera's compatibility with your post-processing software. The images captured by the camera should easily integrate into your photogrammetry software of choice. Ensure that the camera produces image formats (e.g., JPEG, TIFF) supported by your workflow.
FAQ
What is Drone Mapping?
Drone mapping, also known as aerial mapping or UAV (Unmanned Aerial Vehicle) mapping, is a technology-driven process that uses drones equipped with specialized cameras or sensors to capture high-resolution images, data, and geospatial information from the sky.
These images and data are then processed and stitched together to create accurate 2D maps, 3D models, orthomosaics, and point clouds of the Earth's surface.
What is the Average Cost of Drone Mapping?
The average price for drone mapping is typically $100 to $240 per hour. For full-day services, the average cost ranges from $800 to $1,500 per day. These figures can vary based on factors like the complexity of the mapping project, the region or country where the services are provided, the equipment used, and additional services or data processing requirements.
What are the Disadvantages of Drone Mapping?
While drone mapping offers numerous advantages, it also has some disadvantages to consider:
- Regulatory Compliance: Adhering to aviation regulations and obtaining the necessary permits can be complex and time-consuming.
- Weather Dependency: Drone operations are weather-dependent, and adverse weather conditions can disrupt mapping activities.
- Limited Flight Time: Most drones have limited flight times, often between 20 minutes to an hour, which can restrict the coverage area in a single flight.
- Skill and Knowledge Required: Successful drone mapping requires a good understanding of flight operations, camera settings, and post-processing techniques.
- Cost: Acquiring and maintaining quality equipment, software, and certifications can be costly.
What Certifications Do You Need for Drone Mapping?
To legally offer commercial drone mapping services in many countries, you typically need to obtain a remote pilot certificate or license from the relevant aviation authority. For example, in the United States, this is issued by the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA).
To obtain this certification, you must pass a written exam and meet specific eligibility criteria. Additionally, certifications or training related to mapping, photogrammetry, and GIS (Geographic Information Systems) can enhance your expertise and credibility in the field.
What is Needed for Drone Mapping?
For drone mapping, you typically need the following:
- A drone with appropriate sensors (e.g., RGB camera, multispectral camera, LiDAR).
- Remote pilot certification (if operating commercially).
- Mapping software for data processing.
- Ground control points for accuracy.
- A computer for data analysis.
- Knowledge of flight planning and data processing techniques.
How High Should I Fly for a Drone Mapping?
The optimal flying altitude for drone mapping varies based on factors such as the desired ground resolution, the camera's specifications, and the terrain's complexity. In many cases, drones are flown at altitudes ranging from 30 meters (100 feet) to several hundred meters (over 1,000 feet) above the ground. The choice of altitude should aim to achieve the required ground sampling distance (GSD) for your project.
How Accurate is UAV Photogrammetry?
UAV photogrammetry can achieve high levels of accuracy, often within a few centimeters or even millimeters, depending on the equipment, methodology, and ground control points used. The accuracy can meet the requirements of many industries, including agriculture, construction, and surveying.
What's the Best Laptop for Drone Mapping?
The best laptop for drone mapping should have sufficient processing power and memory to handle the data processing demands of mapping software. Look for laptops with high-performance processors (e.g., Intel Core i7 or AMD Ryzen), ample RAM (16GB or more), and dedicated graphics cards.
Which Software is Used for Drone Mapping?
Several software options are commonly used for drone mapping and data processing, including:
- Pix4D: Known for its advanced photogrammetry capabilities.
- Agisoft Metashape (formerly Photoscan): Used for generating 3D models.
- DroneDeploy: Offers cloud-based mapping and analysis.
- Esri ArcGIS: Ideal for GIS (Geographic Information Systems) professionals.