Drone for Bridge Inspection: Benefits, Top Models, and Regulations
Bridges are vital to transportation and the economy, but with heavy use and aging infrastructure, they require frequent and costly repairs.
In the U.S., over a third of bridges need significant repair or replacement, while more than 3,200 in the UK are in disrepair.
As the demand for faster, more efficient inspections grows, drones are emerging as a game-changing solution.
Unlike traditional methods that require lane closures and manual inspections, drones can access hard-to-reach areas without disrupting traffic.
They collect detailed data quickly, enabling advanced inspections for corrosion, structural weaknesses, and even thickness measurements.
In this article, we’ll explore the benefits of drones in bridge inspection, the best tools for the job, and how drones are revolutionizing maintenance in the face of aging infrastructure.

Benefits of Using a Drone for Bridge Inspection
Drones offer a more efficient, safe, and accurate approach to bridge inspections compared to traditional methods.
Enhanced Accessibility and Safety
Drones are game changers when it comes to accessing hard-to-reach areas on bridges. Bridges are often complex structures with tall towers, narrow beams, and undersides that are challenging or dangerous to inspect manually.
Traditional methods require workers to physically access these areas, often with scaffolding, cranes, or ropes, which can be risky and time-consuming.
With drones, inspectors can fly close to these difficult spots—like the underside of a suspension bridge or over water—without needing to put anyone in harm’s way. This drastically reduces the risk of falls or accidents.
Improved Efficiency and Cost-Effectiveness
Drone inspections are significantly faster and cheaper than traditional methods. A typical bridge inspection can take days or even weeks, especially when scaffolding or heavy machinery is involved. Drones, however, can complete the same task in a matter of hours. In many cases, drones can cut inspection times by up to 75%.
Cost savings are another big plus. Traditional bridge inspections can cost anywhere from $4,500 to $10,000 per bridge, depending on the size and complexity of the structure.
Drones eliminate the need for much of the expensive equipment and labor, bringing down costs significantly. Some reports indicate that drones can save up to 40% on inspection costs, meaning agencies can redirect those funds to other maintenance tasks.
Enhanced Data Collection and Analysis
Drones significantly enhance data collection for bridge inspections through advanced imaging technologies. High-resolution cameras capture detailed images of bridges, allowing inspectors to detect even the smallest defects, such as cracks and corrosion, that might be missed by manual inspection.
Thermal imaging provides an additional layer of analysis, detecting temperature anomalies that indicate hidden structural issues, such as water ingress or material degradation.
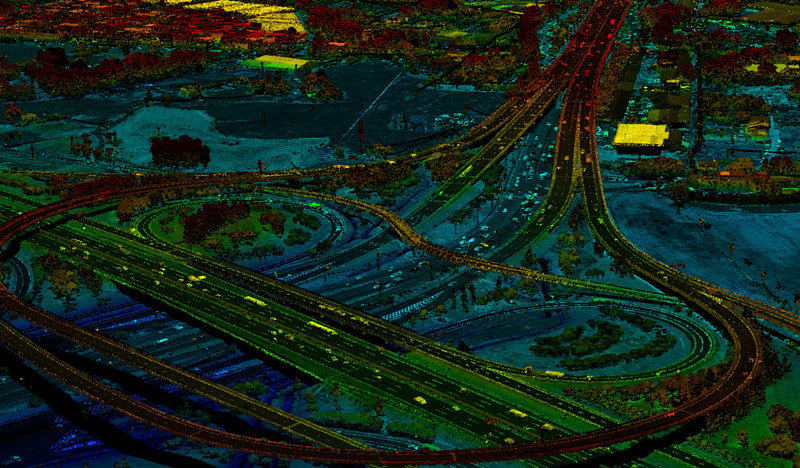
Drones also enable the creation of accurate 3D models using LiDAR technology. These models allow engineers to analyze a bridge from multiple angles, taking precise measurements and tracking changes over time.
Improved Accuracy and Precision
Manual inspections are limited by human error and the physical ability of workers to access all areas of the structure. In contrast, drones can fly to within inches of a bridge’s surface, capturing detailed images and generating 3D models with extreme precision.
For example, LiDAR-equipped drones can detect deviations as small as 1 cm in structural components, making it easier to identify early signs of deterioration, such as surface cracks or material displacement.
Real-Time Monitoring and Early Detection
By conducting regular inspections, drones can identify potential problems before they escalate into serious safety hazards. This proactive approach allows maintenance teams to address minor repairs quickly, saving time and money in the long run.
In addition to regular inspections, many advanced drones are equipped with sensors that enable real-time monitoring of a bridge's health. These sensors can track vital parameters such as vibrations, temperature changes, and structural movement.
For instance, if a drone detects unusual vibrations or shifts in a bridge during high traffic or severe weather, it can send immediate alerts to engineers. This allows for quick assessments and interventions, preventing small issues from developing into major problems.
The PH-20's gimbal camera allows for stable, high-quality video and images, making it perfect for monitoring traffic flow and conducting safety inspections on bridges.
Best Drones for Bridge Inspection
When selecting a drone for bridge inspection, it's essential to consider factors such as payload capacity, flight endurance, range, and camera quality.
JOUAV PH-20
| Pros | Cons |
|
|

The JOUAV PH-20 is a robust drone designed for heavy payload operations, capable of carrying up to 10 kg of sensors, including high-resolution cameras and LiDAR systems. Its impressive flight time of up to 75 minutes is particularly beneficial for inspecting large bridges, as it minimizes battery changes and maximizes coverage per flight.
Equipped with a high-resolution thermal camera, the PH-20 allows inspectors to detect heat anomalies indicative of structural issues like fatigue or insulation failures. The drone incorporates AI technology for automatic defect detection, enhancing inspection efficiency. Additionally, its RTK (Real-Time Kinematic) positioning system ensures centimeter-level accuracy, critical for assessing bridge integrity.
The PH-20 is designed for durability, boasting an IP55 rating for water and dust resistance, which enables inspections in challenging weather conditions. Its integrated obstacle avoidance system further enhances safety by allowing navigation around complex structures. Overall, the JOUAV PH-20 is an excellent choice for comprehensive and reliable bridge inspections.
DJI Matrice 300 RTK
| Pros | Cons |
|
|

The Matrice 300 RTK's 55-minute flight time allows it to complete most bridge inspections in one go, minimizing the need for battery changes, which is especially useful for long or remote bridges.
Equipped with the H20 hybrid camera, which includes a 20MP zoom, 12MP wide-angle, thermal camera, and laser rangefinder, it captures detailed visual and thermal data, making it easier to detect surface and internal structural issues.
Its RTK system provides real-time GPS accuracy, eliminating the need for ground control points (GCPs) and enabling efficient data collection, especially for bridges where GCPs are hard to place.
AI-powered spot-checks automate routine inspections, ensuring consistency in tracking corrosion, cracks, or stress over time, and enhancing long-term maintenance planning. With an upward gimbal, the Matrice 300 RTK allows inspectors to easily view hard-to-reach areas like the underside of bridges, reducing the need for scaffolding.
Its 15km transmission range ensures safe operation in challenging environments, like remote or obstructed bridge sites. The drone’s durability, operating in temperatures from -20°C to +50°C, ensures reliable performance in extreme weather, allowing inspections to stay on schedule.
Autel Evo 2 Pro RTK
| Pros | Cons |
|
|

The Autel Evo 2 Pro RTK is a more affordable yet powerful option for bridge inspections. It offers a flight time of approximately 40 minutes and supports high-resolution imaging with its 6K video capabilities. This drone is particularly appealing for teams looking for quality data without breaking the bank.
The Evo 2 Pro RTK is equipped with both RTK and PPK (Post-Processed Kinematic) systems, enhancing the accuracy of the data collected during inspections. This precision is especially important when assessing structural integrity and pinpointing any areas of concern. The drone's obstacle avoidance technology further adds to its safety, allowing it to navigate around complex bridge structures without risk.
Thermal imaging capabilities are another key feature of the Evo 2 Pro RTK. This function enables inspectors to detect temperature variations that could indicate underlying structural issues, making it a valuable tool for comprehensive assessments.
Skydio 2+
| Pros | Cons |
|
|
The Skydio 2+ distinguishes itself through its advanced autonomous flying capabilities. It is designed to navigate complex environments on its own, which can be particularly beneficial when inspecting intricate bridge designs. Its ability to fly autonomously reduces the need for skilled pilots, making it accessible for a broader range of users.
This drone features a 4K HDR camera that captures high-quality images and videos, providing inspectors with the detailed visuals necessary for thorough assessments. Although it has a shorter flight time of around 27 minutes, its autonomous capabilities allow it to maximize the coverage of each flight, making it efficient for bridge inspections.
The Skydio 2+ is ideal for situations where safety is a concern, as its AI technology allows it to avoid obstacles in real-time. This makes it especially useful for inspecting hard-to-reach areas where traditional methods might pose risks to personnel.
DJI Mavic 3 Enterprise Thermal
| Pros | Cons |
|
|

The DJI Mavic 3 Enterprise Thermal is a compact and versatile drone suitable for a variety of inspection tasks, including bridges. With a flight time of up to 45 minutes, it strikes a balance between performance and portability. It offers multiple camera options, including a thermal sensor and a high-resolution visual camera, enabling comprehensive data collection during inspections.
The Mavic 3 Enterprise Thermal is particularly advantageous for teams that require a quick deployment. Its lightweight design makes it easy to transport, and it can be quickly set up for inspections, which is especially valuable in emergency situations. The user-friendly interface allows for seamless operation, even for those with limited experience in drone piloting.
Flyability Elios 3
| Pros | Cons |
|
|

The Elios 3 is a unique drone designed for inspections in confined spaces, making it particularly well-suited for complex bridge structures. Its protective frame allows it to navigate tight areas without risk of damage, which is essential for thorough evaluations of intricate designs. The drone is equipped with both HD and thermal cameras, enabling inspectors to capture critical data on a bridge's structural condition.
One of the most remarkable features of the Elios 3 is its ability to capture upward shots with a 180° gimbal. This capability is invaluable for inspecting under-bridge structures, where traditional access may be limited. Additionally, its durability allows it to operate in a wide range of temperatures and environmental conditions, ensuring reliable performance during inspections.
The Process of Drone Bridge Inspection
Drone bridge inspection typically involves pre-planning, drone preparation, data collection, post-flight data processing, report generation, and data archiving.
Planning starts by defining inspection objectives based on the bridge's size, age, and any known issues. Inspectors then choose the appropriate drone and equipment, like high-resolution cameras or thermal sensors.
Next is pre-flight preparation, where a checklist ensures all drone systems are operational. Inspectors check battery levels, and camera settings, and assess weather conditions to ensure safe flying.
During the inspection, drones follow pre-programmed flight paths to capture high-resolution images and videos from various angles. Thermal sensors detect temperature anomalies that may indicate structural problems, while high-resolution cameras identify cracks and surface defects.
After data collection, inspectors move to data analysis. Specialized software analyzes the images, often using AI to flag potential issues, making it easier to assess the bridge's condition.
Finally, a comprehensive inspection report is generated, detailing findings, photographs, and maintenance recommendations. This report is essential for engineers and stakeholders, helping them understand the bridge's state and plan for necessary repairs.
Applications of Drone Bridge Inspection
Drones have revolutionized bridge inspections by offering a range of applications that enhance safety, efficiency, and data quality.
- Visual Inspections: Drones equipped with high-resolution cameras can capture detailed images and videos of a bridge's structure. This allows inspectors to identify visible defects such as cracks, corrosion, and delamination from multiple angles without the need for scaffolding or cranes.
- Thermal Inspections: Drones fitted with thermal imaging cameras can detect temperature variations on a bridge's surface, which may indicate underlying issues such as moisture intrusion, heat loss, or insulation failures. This application is particularly useful for assessing the integrity of bridge components that are not easily visible.
- Structural Monitoring: Drones can be used for continuous or periodic monitoring of bridges. By collecting data over time, they help track structural changes and performance, allowing engineers to identify trends that could indicate potential failures. This long-term monitoring is crucial for aging infrastructure.
- Load Testing: Drones can assist in load testing by providing aerial views of a bridge under various weight conditions. This helps engineers analyze the bridge's response to loads, ensuring it meets safety standards and can handle the required traffic.
- Surveying and Mapping: Drones equipped with LiDAR or photogrammetry capabilities can create highly accurate 3D models of bridges and their surroundings. This data is valuable for planning maintenance, repairs, or even new construction projects, offering precise measurements that are difficult to achieve through traditional methods.
- Emergency Response: In cases of natural disasters or accidents, emergency drones can quickly assess damage to bridges. This rapid evaluation helps emergency services prioritize responses and determine the safety of the structure for rescue operations or traffic flow.
Bridge Construction Projects Utilizing Drones
Here are some notable examples of bridge construction projects utilizing drones:
Golden Gate Bridge Seismic Retrofit
The Golden Gate Bridge, completed in 1937, spans about 1.7 miles in San Francisco. Due to its age and seismic risk, a major retrofit project was launched to improve its earthquake resilience.
Drones were used for detailed inspections of the bridge’s structural components, like cables and anchorages. With high-resolution cameras, they provided crucial imagery that minimized the need for scaffolding, reducing traffic disruptions. Drones also aided in topographical surveys, facilitating better planning for construction logistics.
San Francisco-Oakland Bay Bridge Replacement
The San Francisco-Oakland Bay Bridge, a critical transportation link, connects San Francisco and Oakland. Following damage from the 1989 earthquake, a new eastern span was constructed, completed in 2013.
Drones conducted aerial surveys to monitor construction progress and assess structural integrity. Equipped with LiDAR, they provided precise mapping, which informed design and planning decisions. This technology-enhanced safety by allowing engineers to identify issues from a distance, minimizing the need for close-up inspections.
New River Gorge Bridge Replacement
The New River Gorge Bridge in West Virginia, spanning 3,030 feet, is one of the longest arch bridges. A replacement project was initiated to upgrade its safety and extend its lifespan.
Drones were instrumental in inspecting the existing bridge, capturing detailed imagery to spot wear and potential issues. They also facilitated mapping and surveying of the area, ensuring accurate data for the design phase. This use of drones improved efficiency and reduced environmental impact during the replacement process.
Drone Regulations for Bridge Inspections
Drone operations for bridge inspections are subject to various regulations aimed at ensuring safety and compliance. Each country has its aviation authority with specific requirements, which can differ widely.
In the United States, commercial drone operations are governed by the FAA’s Part 107 regulations. To operate legally, pilots must obtain a Remote Pilot Certificate by passing a written exam and meeting eligibility criteria. Drones over 0.55 pounds must also be registered with the FAA.
Part 107 includes operational limitations: drones must be flown during daylight, operators must maintain a visual line of sight, and there's a 400-foot altitude limit to prevent conflicts with manned aircraft. Drones cannot operate in controlled airspace, such as near airports, without prior authorization.
For bridge inspections, operators may need additional waivers for flying beyond the visual line of sight or in controlled airspace, requiring a detailed application outlining operational plans.
Local laws may impose further restrictions, particularly in urban areas or near critical infrastructure. Operators should be aware of these local regulations to avoid fines and ensure safe operations.
FAQ
Can You Fly a Drone Near a Bridge?
Flying a drone near a bridge is subject to specific regulations and restrictions. In the United States, the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) prohibits drone operations in controlled airspace without authorization, which often includes areas around bridges, especially if they are near airports or urban centers.
Can I Fly a Drone Near the Golden Gate Bridge?
Flying a drone near the Golden Gate Bridge is generally prohibited. The National Park Service, which manages the Golden Gate Bridge, has strict regulations regarding drone operations in the area.
It is important to check the specific regulations and obtain any necessary permits before attempting to fly a drone near the bridge.
Can You Fly a Drone Under a Bridge?
Flying a drone under a bridge is generally discouraged due to the risk of collisions and potential interference with bridge operations.
However, in some cases, it may be possible to obtain permission to fly a drone under a bridge for specific purposes, such as inspections or research.
How Often Are Bridges Inspected?
The frequency of bridge inspections varies depending on factors such as the age of the bridge, its traffic volume, and its structural condition.
In the United States, the Federal Highway Administration (FHWA) recommends that bridges be inspected at least once every two years.
However, some bridges may require more frequent inspections, especially if they are located in areas with high seismic activity or other risk factors.
What Tool Do You Use to Detect Delamination?
Delamination is a type of structural damage that occurs when layers of a material separate. There are several tools that can be used to detect delamination in bridges, including:
- Visual Inspection: Visual inspections can be conducted by trained personnel to identify signs of delamination, such as cracks, bulges, or discoloration.
- Ultrasonic Testing: Ultrasonic testing uses sound waves to detect delamination and other defects in materials.
- Infrared Thermography: Infrared thermography can detect temperature anomalies that may indicate delamination or other structural problems.
- Ground Penetrating Radar (GPR): GPR can be used to detect delamination and other subsurface defects in concrete structures.