Cattle Rustling: Causes, Prevention, Punishment
Cattle rustling, also known as cattle raiding, is the theft of livestock, primarily cattle. This age-old crime has plagued ranchers for centuries, causing significant economic hardship and disrupting food supply chains.
In the wild west of the 19th century, particularly in regions like Texas and Oregon with vast, open ranges and limited law enforcement, cattle rustling ran rampant. Rustlers could easily stampede or drive off entire herds under the cover of darkness. While the image of the dusty desperado might be outdated, this age-old crime persists globally.
Beyond the US, cattle rustling continues to plague ranchers across the globe:
- Cattle rustling has a long history in East Africa, particularly countries like Kenya, Uganda, and South Sudan. Here, cultural practices, competition for scarce resources like grazing land and water, and the easy availability of weapons fuel this crime.
- West Africa is seeing a rise in cattle thefts, often motivated by criminal gain. Stolen animals are sold in urban markets, feeding a black market for livestock.
- Border regions in Latin America are particularly vulnerable, with stolen cattle easily smuggled to neighboring countries with higher market prices.
Modern rustlers have adapted their methods, often employing trucks for faster transportation and, in some cases, using sophisticated techniques like anesthetization for quieter operations.
In California alone, ranchers lose an average of about 1,900 head of cattle each year, resulting in an estimated $1.5 million in losses. However, only about half of the stolen animals are recovered by law enforcement.

Causes of Cattle Rustling
The motivations behind this crime extend far beyond a simple desire for profit. Here's a detailed breakdown of the key factors that contribute to modern-day cattle rustling:
Financial Gain
Profit remains a primary motivator. Cattle are valuable assets, and their illegal sale offers a tempting source of income, especially in regions with weak economies or limited job opportunities. Poverty among youth can further push them towards rustling as a means of survival.
Organized Crime
Cattle rustling isn't limited to individual opportunists. In some areas, organized crime networks steal cattle on a large scale, feeding black markets for meat and leather.
Rising Cattle Prices
An increase in the market value of cattle can incentivize theft, making rustling a more lucrative endeavor for criminals.

Social Status
In some cultures, owning large herds signifies wealth and social standing. Stealing cattle can be a way for individuals, particularly younger generations, to gain recognition and establish themselves within the community.
Political Instigation
In some cases, politicians may use bribery to involve rural communities in cattle rustling. This can be a way to raise money for campaigns or to target supporters of rival political figures.
Weak Security Systems
Ungoverned spaces, weak law enforcement, and porous borders create a safe haven for rustlers and make it difficult to apprehend them. Inadequate state presence in remote areas further exacerbates the problem.
Weak Legislations
Lax laws with insufficient penalties for cattle rustling can create a disincentive for apprehension and prosecution, emboldening criminals.
Historical Practices
While fading, remnants of historical practices like cattle raiding in certain cultures can influence modern rustling, especially in regions with strong cultural traditions.
Competition for Resources
Scarcity of resources like grazing land and water can lead to cattle rustling as a means to acquire these vital assets for one's own herd, particularly during periods of drought or environmental stress.

Socio-cultural Perceptions
Certain cultural norms or beliefs may downplay the severity of cattle rustling or even glorify it, making it a more socially acceptable act in some communities.
Proliferation of Guns
Easy access to firearms or other weapons makes cattle rustling a more viable and potentially less risky option for criminals.
How to Prevent Cattle Rustling?
Here's a breakdown of strategies to prevent cattle rustling, combining traditional methods, technological advancements, community collaboration, and additional security measures:
Know Your Cattle
Daily visits and head counts are crucial. The longer a missing animal goes unreported, the more difficult it will be to track down the rustler. Vary your visit and feeding times to deter potential rustlers from predicting your schedule.
Maintain Fences and Gates
For starters, build pens away from the roadway and conceal them if possible. Secure your enclosures with strong locks and capped hinges. Regularly inspect for damages or weak links in fences that might allow access.

Be Observant
Trust your gut. If you see signs of someone on your property, footprints, tire tracks near the perimeter, suspicious vehicles making repeat visits, or slowing down near your land, take extra precautions and report it to authorities.
Mark Your Livestock
Whether you use a brand, tattoo, or tag system, clearly mark your animals. Markings deter theft by making animals difficult to sell and linking them back to you. Branding is a time-tested method with many states maintaining registries.
Security Cameras
Strategically placed security cameras with night vision capabilities can deter rustlers and provide valuable evidence.
Cattle Monitoring Systems
Electronic ear tags or implants with radio-frequency identification (RFID) chips can track cattle movement and alert ranchers if animals leave designated areas. This technology helps in pinpointing stolen livestock and notifying authorities quickly.

GPS Tracking
GPS collars attached to cattle provide real-time location data, allowing ranchers to track their herd's movement in real time. This can be beneficial in identifying unusual movements that might indicate potential rustling attempts.
Neighborhood Watch Programs
Collaboration with neighboring ranchers and establishing a communication network is extremely helpful. Sharing information about suspicious activity or sightings of unfamiliar vehicles near ranch lands can significantly improve overall security.

Law Enforcement Partnerships
Building strong relationships with local law enforcement is key. Regular communication, sharing information about cattle rustling trends in the area, and participating in joint patrols can lead to more effective prevention and apprehension of rustlers.
Licensing and Registration
Implementing a system for licensing and registering cattle in a specific region can make tracking stolen animals easier and discourage rustling.
Public Awareness Campaigns
Raising public awareness about cattle rustling through educational campaigns can help deter potential buyers of stolen livestock, disrupting the economic incentive for theft.
How Drones Help Combat Cattle Rustling?
Drones are revolutionizing ranch security by offering cost-effective, real-time monitoring capabilities. Here's a breakdown of their specific applications and impactful data collection:
Cost-Effective Patrols
Compared to traditional ground patrols, drones excel at covering large distances quickly and efficiently. A single drone flight can survey hundreds of acres in a fraction of the time it takes on foot or horseback. Advanced models, like the JOUAV PH-20, boast coverage exceeding 700 hectares per flight. This translates to areas that would take hours or even days to patrol on the ground being covered in minutes, significantly increasing patrol frequency.
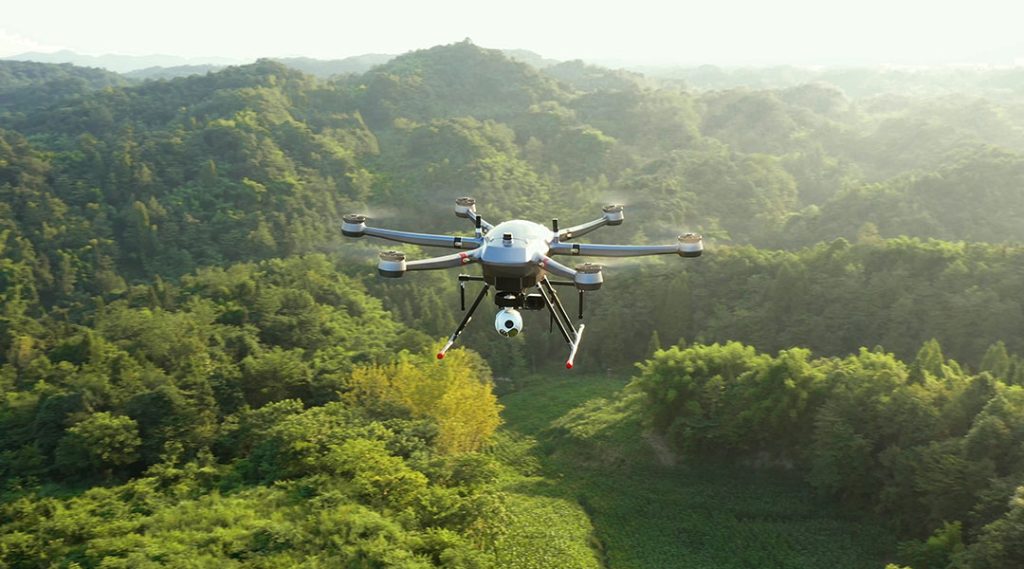

The lower operational costs of drone patrols allow ranchers to conduct more frequent checks on their land. This increased vigilance acts as a strong deterrent to potential rustlers, who are less likely to attempt theft if they believe the chance of early detection is high.
Real-Time Monitoring & Early Detection
Drones equipped with high-definition cameras can provide live video feeds directly to a rancher's smartphone or tablet. This allows for:
- Immediate Response: If suspicious activity is spotted during drone surveillance, ranchers can alert authorities or security personnel immediately, potentially apprehending rustlers before they steal any cattle.
- Early Warning Signs: Drones with Artificial Intelligence (AI) technology can identify signs of tampering with fences, unauthorized access points, or unusual animal movement, allowing ranchers to intervene before a theft occurs.
![]()
The PH-20 equipped with MG-120E utilizes integrated AI to recognize a variety of objects in real-time, including people, animals, vehicles, boats, and even fire points. Beyond object recognition, the system can also automatically count objects within the camera's field of view.
One of our happy rancher customers reported a dramatic 75% reduction in cattle rustling on their ranch after implementing the PH-20 drone equipped with the MG-120E dual-light gimbal camera for real-time surveillance.
Aerial Footage & Data Collection
Drones can capture high-resolution aerial photographs and videos of cattle and their surroundings. This data can be used for:
- Missing Cattle: Drones can quickly scan large areas to locate missing animals, especially those lost in rough terrain or dense vegetation.
- Herd Management: Aerial footage can be used to track herd movement patterns, assess pasture health, and identify areas where cattle may be congregating due to a lack of water or grazing resources.
- Improved Decision-Making: Data collected by drones can help ranchers make informed decisions about grazing management, resource allocation, and overall herd health.
Reduced Risk & Improved Safety
Drones allow ranchers to check remote areas of their property without putting themselves in potential danger. This is particularly beneficial for:
- Difficult Terrain: Drones can easily navigate rough terrain, steep slopes, or dense brush that would be hazardous to access on foot or horseback.
- Wildlife Encounters: Ranchers can avoid potential encounters with dangerous wildlife by using drones to scout areas before entering on foot.
What is the Penalty for Cattle Rustling?
In the United States, cattle rustling remains a serious offense with penalties that vary significantly depending on several key factors.
Federal vs. State Laws
Federal Law: There's a limited federal statute (18 U.S. Code § 667) that applies to cattle rustling only if the stolen livestock has a value of $10,000 or more and crosses state lines (becomes interstate commerce). A conviction under this statute can lead to fines or imprisonment for up to five years or both.
State Laws: Cattle rustling penalties are primarily determined by state laws. These laws can differ significantly, so researching the specifics in your state is crucial. Here's how some factors can influence the penalty:
- Value of Stolen Livestock: Most states have tiered penalties based on the value of the stolen cattle. The higher the value, the harsher the punishment. Some states might classify theft under a certain dollar amount as a misdemeanor (fines, community service), while thefts exceeding that amount become felonies (prison time, fines).
- Number of Animals Stolen: Similar to value, the number of animals stolen can also impact the severity of the crime. Stealing a single cow might carry a lesser penalty compared to rustling an entire herd.
- Prior Offenses: Repeat offenders for cattle rustling will likely face steeper penalties due to a history of criminal activity.

Examples of State Cattle Rustling Penalties
Texas: Texas classifies cattle theft as a felony if the value of the stolen livestock exceeds $150. The potential penalties range from state jail felony (180 days to 2 years) for lower values to second-degree felony (2-20 years) for thefts exceeding a certain threshold.
Montana: Montana's cattle theft laws are based on the value of the stolen animal(s). For instance, stealing a single animal under $1,500 might be a misdemeanor, while theft exceeding $1,500 becomes a felony with potential prison sentences.
Finding Specific Information
Here are resources to find the exact penalties for cattle rustling in your jurisdiction:
- Local Law Enforcement: Contacting your local sheriff's department or police department is the most reliable way to get up-to-date information on cattle rustling penalties in your specific area.
- State Government Websites: Many state government websites have legal information sections that outline penalties for livestock theft. Search for terms like "cattle theft statutes" or "livestock theft penalties" on your state's official website.
FAQ
Can You Still be Hung for Cattle Rustling?
No, in the vast majority of places, you cannot be hanged for cattle rustling in the modern era. While cattle rustling was a serious offense in the past, capital punishment (death penalty) for this crime is no longer practiced.