The Ultimate Guide to Autonomous Drones: Benefits, Applications, and Top Models
Autonomous drones have revolutionized the way we perceive aerial capabilities. Gone are the days when human pilots were solely responsible for navigating the skies. With advancements in artificial intelligence, computer vision, and robotics, drones have transcended mere remote-controlled gadgets to become intelligent, self-governing aerial companions.
From aerial photography and videography to search and rescue operations, agricultural monitoring, and delivery services, drone autonomy is transforming industries and reshaping our daily lives.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the world of autonomous drones, exploring their functionality, components, advantages, and diverse applications across industries, and showcase the top fully autonomous drones currently on the market.
Are you ready to embark on this exciting journey?
Let's dive right in!
What is an Autonomous Drone?
An autonomous drone refers to a cutting-edge unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) equipped with advanced technologies that enable it to operate independently, without the need for constant human intervention. These drones possess the capability to perform tasks and navigate through environments autonomously, relying on a combination of sensors, artificial intelligence (AI), and sophisticated algorithms.
Depending on the level of autonomy, autonomous drones can have different capabilities. Some drones may require pre-programmed flight plans, where the route and actions are determined in advance. Others are capable of real-time decision-making, using artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms and machine learning techniques to analyze sensor data and respond to changing conditions. These advanced autonomous drones can adapt their flight path, avoid obstacles, track targets, and perform complex tasks without continuous human input.

How Does an Autonomous Drone Work?
What is the functioning principle of an autonomous drone? Essentially, it operates in a similar manner to a drone controlled remotely. An operator can still maneuver the drone using a controller, and in certain cases, this method is preferred over relying on autonomous flight modes. It's worth noting that controlling the drone through a tablet or smartphone is also a possibility.
The key distinction of an autonomous drone is its ability to continue flying independently once the piloting phase is completed. This relieves the operator from the need to manually bring the drone back home, saving valuable time. By configuring a specific flight path or diverting attention to other tasks, the autonomous software will continue operating until instructed otherwise.
What are the Components of Autonomous Drones?
While many components are shared between autonomous drones and other types of drones, some components are specifically tailored for autonomous functionality. The following components are particularly crucial for autonomous drones:
- Autopilot System: The autopilot system is a specialized component that allows autonomous drones to operate without constant human control. It consists of software and hardware that process sensor data, execute flight plans, and make autonomous decisions.
- GPS Module: The GPS module plays a crucial role in autonomous drones by providing accurate positioning data. It allows the drone to navigate autonomously, follow pre-defined flight paths, and perform tasks with precision.
- Sensors: Autonomous drones typically incorporate additional sensors beyond the basic ones found in non-autonomous drones. These may include obstacle avoidance sensors (such as ultrasonic or LiDAR sensors), optical sensors for visual recognition and mapping, and other specialized sensors depending on the drone's intended application.
- Onboard Computer: An autonomous drone requires a powerful onboard computer capable of running sophisticated algorithms and processing large amounts of data in real-time. This computer is responsible for decision-making, path planning, and executing autonomous flight tasks.
These components work in tandem to enable autonomous drones to operate independently, make decisions based on their surroundings, and carry out complex tasks without direct human intervention.
What are the Advantages of Autonomous Drones?
The primary purpose of autonomous drones is to perform a wide array of tasks efficiently and without direct human control. The advantages of utilizing autonomous drones include:
Enhanced Safety and Risk Mitigation:
One of the primary advantages of autonomous drones lies in their ability to significantly improve safety in various applications. By eliminating the need for human pilots, autonomous drones can perform intricate tasks with precision, reducing the risk of accidents and injuries. Moreover, these drones can navigate challenging environments and hazardous conditions, such as disaster zones or industrial sites, without jeopardizing human lives.
Increased Efficiency and Productivity:
Autonomous drones offer a substantial boost in efficiency and productivity across multiple industries. With their advanced sensors and imaging capabilities, these drones can swiftly and accurately gather data, conduct inspections, and monitor vast areas that would otherwise require extensive human resources and time. For example, in agriculture, autonomous drones can efficiently survey crops, identify crop health issues, and optimize irrigation strategies, resulting in improved yield and reduced resource wastage.
Cost Savings:
Implementing autonomous drone technology can lead to significant cost savings for businesses. By automating various tasks, companies can minimize labor costs associated with manual inspections, surveys, and data collection. Additionally, the use of autonomous drones can reduce the need for expensive equipment and infrastructure, further lowering operational expenses. These cost savings make autonomous drones an attractive option for businesses looking to optimize their operations without compromising quality.
Applications of Autonomous Drone
Autonomous drones have revolutionized a wide range of industries with their advanced capabilities. Let's discover together!
Surveillance and Security
Autonomous drones have become indispensable for surveillance and security tasks, bringing heightened safety and monitoring capabilities. With their high-resolution cameras and advanced sensors, these security drones can effortlessly patrol areas, monitor activities, and relay real-time video feeds to security personnel. Homeowners can now remotely monitor their properties, while businesses benefit from an extra layer of protection. The watchful presence of autonomous home security drones deters intruders, making our living spaces safer.
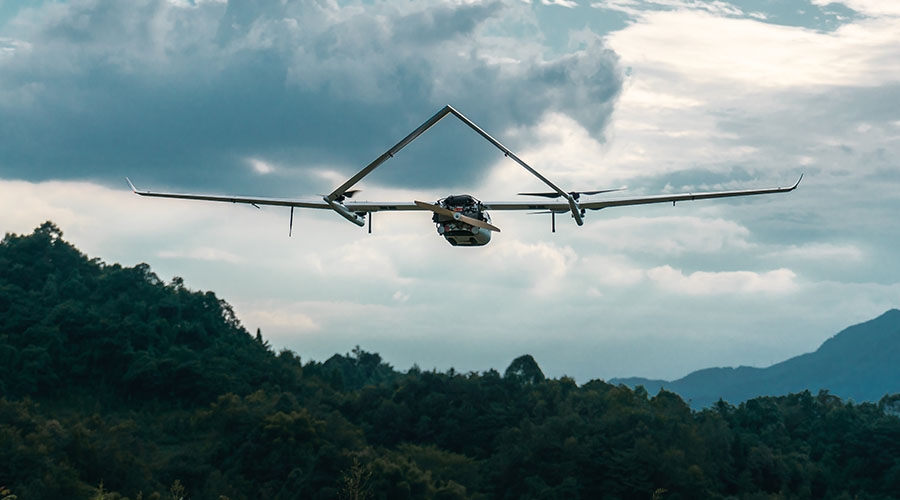

Mapping and Surveying
Mapping and surveying tasks have been revolutionized by autonomous drones, making data collection and analysis more efficient than ever before. These survey drones expertly capture aerial imagery, create detailed maps, and even generate 3D models of various terrains and structures. Urban planners, land surveyors, and construction companies benefit from the accuracy and ease of data gathering, leading to better-informed decisions and streamlined projects.
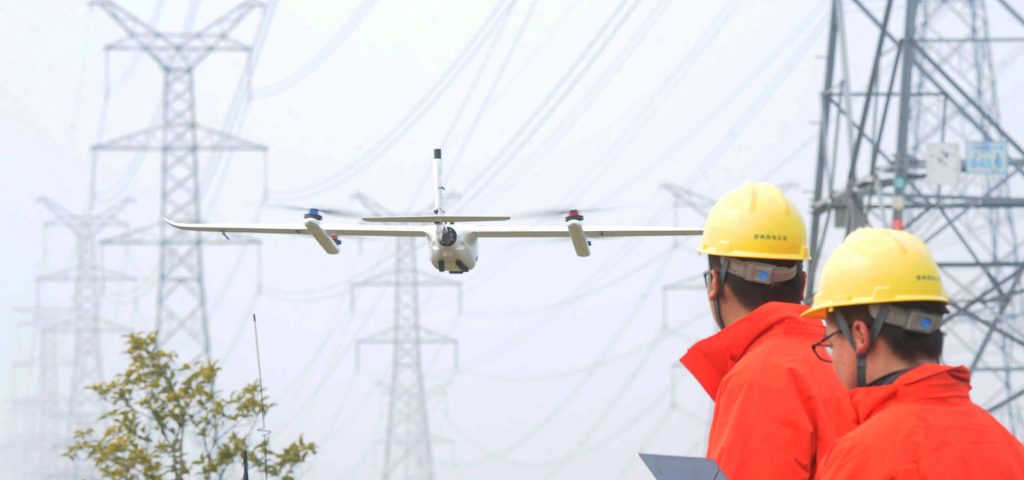
Equipment Inspection
Autonomous drones are invaluable for equipment inspection, including power lines, pipelines, and blades in wind turbines. They can autonomously navigate complex structures, capturing high-quality visual data. By conducting inspections without human intervention, these drones minimize risks, improve safety, and enhance the efficiency of maintenance operations. They detect anomalies, identify potential issues, and contribute to proactive maintenance strategies.

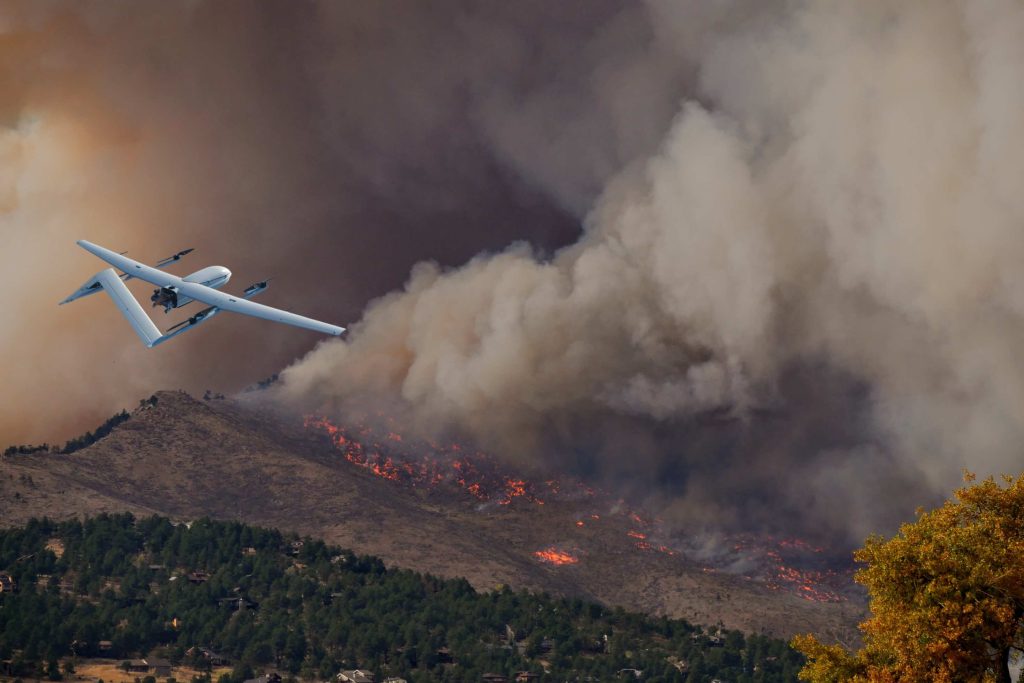
Disaster Response
In disaster response scenarios, autonomous drones play a crucial role by providing real-time situational awareness and supporting emergency services. Firefighting drones, equipped with thermal cameras and fire suppression systems, assess wildfires, identify hotspots, and aid firefighting efforts. These drones navigate hazardous environments, assisting decision-making and facilitating efficient disaster response.

Agriculture
The agricultural sector has embraced autonomous drones to optimize crop management. These drones can be equipped with various sensors and imaging systems to monitor crop health, detect irrigation needs, and assess soil conditions. By capturing valuable data and generating detailed aerial maps, autonomous agriculture drones enable farmers to make informed decisions. They facilitate targeted pesticide application, irrigation, and crop monitoring, leading to improved yields, reduced costs, and sustainable farming practices.
Military Operations
The military sector benefits from autonomous drones for intelligence gathering, surveillance, and reconnaissance missions. These drones can be deployed in remote or hostile areas, collecting vital information and monitoring activities in real-time. With their stealthy nature and advanced imaging capabilities, autonomous military drones offer valuable situational awareness to commanders, aiding in mission planning, threat assessment, and target identification. They minimize the risks to military personnel and enhance operational efficiency.
Delivery
Autonomous drone delivery services are revolutionizing the logistics industry, particularly for last-mile delivery. These drones navigate through urban environments and congested areas, offering swift and efficient delivery of small packages. With their ability to bypass traffic and provide faster delivery times, autonomous drone delivery services improve logistics efficiency and customer satisfaction.
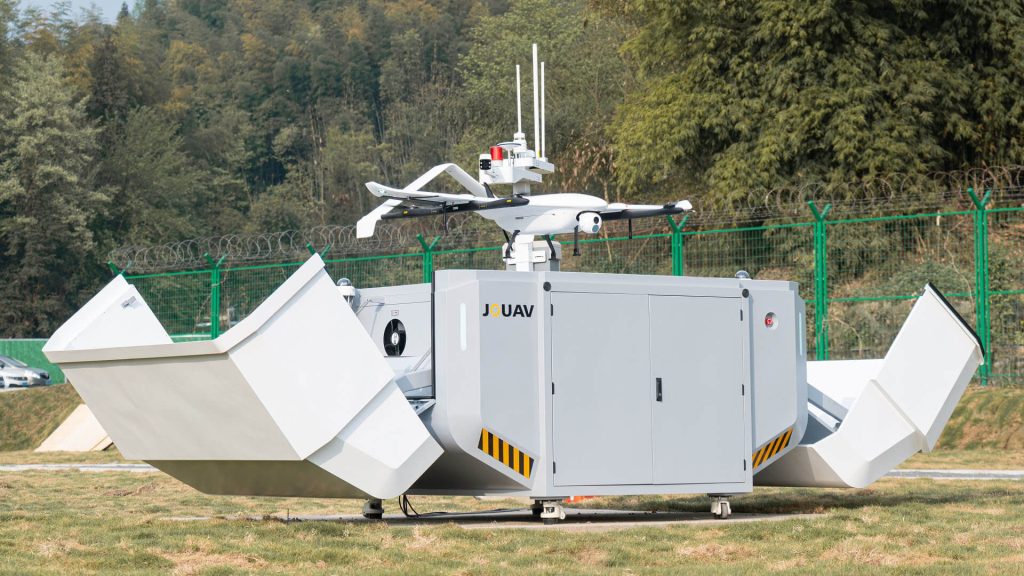
Best Fully Autonomous Drones for Industrial Sites - JOUAV VTOL Hangar
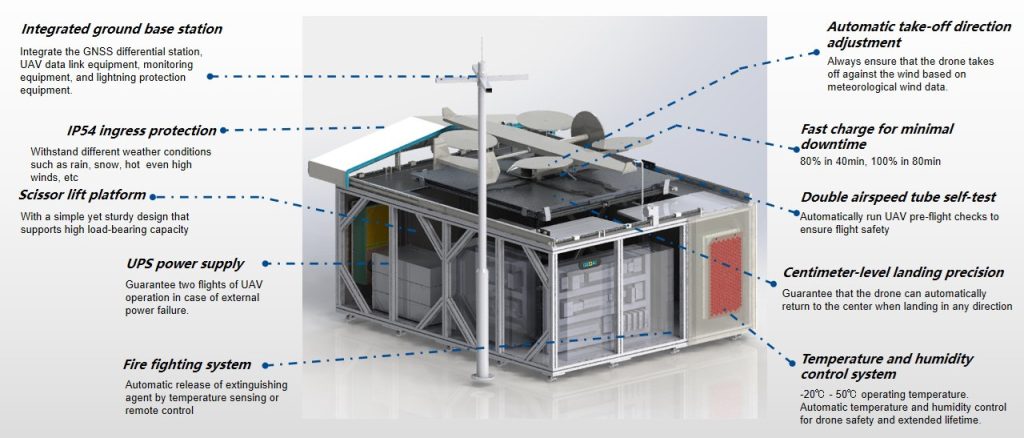
Designed specifically for large-scale industrial sites, the JOUAV VTOL Hangar is a leading solution that offers an all-in-one package for industrial inspections. As a drone-in-a-box system, it provides fully autonomous capabilities, long-range flight, obstacle avoidance, and advanced data analysis.
Fully Autonomous Drone-in-a-Box Solution
The JOUAV VTOL Hangar comprises three main components: the CW-15V autonomous VTOL drone, the JOS-C800 drone station (commonly known as "the box"), and the Jocloud AI-powered software. This integrated system ensures immediate availability on-site, enabling efficient and frequent inspections. With its autonomous capabilities, the drone-in-a-box solution eliminates the need for a ground-based controller or human pilot, making it an ideal choice for continuous and persistent data collection.
Long-Range Autonomous Flight
Equipped with the CW-15V VTOL drone, the JOUAV VTOL Hangar offers impressive flight endurance and range. With a maximum flight time of 180 minutes and a cruising speed of 72 km/h, the drone can cover large areas in a single mission. Its long-range capabilities make it suitable for inspections of expansive industrial sites, infrastructure, and remote locations, providing comprehensive visual data and insights.
Advanced Obstacle Avoidance
Safety is paramount in autonomous drone operations, and the JOUAV VTOL Hangar incorporates advanced obstacle avoidance technology. With its precise landing system using RTK+ Visual Guidance, the drone can detect and avoid obstacles during flight, ensuring smooth and reliable operations even in complex environments. This feature minimizes the risk of collisions and maximizes the safety of both the drone and the inspected assets.
Seamless Self-Flying and Self-Piloting
The JOUAV VTOL Hangar's autonomous capabilities extend to self-flying and self-piloting functions. By utilizing the Jocloud AI-powered software, operators can program flight paths, schedule missions, and request specific data collection on any computer from any location. Once activated, the drone takes off autonomously from the box, performs the assigned tasks, and returns home upon completion. This seamless self-flying and self-piloting process eliminates the need for constant human intervention and enables efficient data collection without delays.
Real-Time Monitoring and Data Analysis
The JOS-C800 drone station acts as more than just a landing pad and charging station. It also serves as a data hub, enabling real-time video monitoring and environmental sensing, including temperature, humidity, rainfall, and wind direction. During missions, stakeholders can remotely monitor site conditions in real time and receive alerts and operational insights. The system can also generate automated reports based on mission findings, facilitating data analysis and post-inspection reviews.
FAA Autonomous Drone Regulations
The Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) in the United States has established regulations and guidelines specific to autonomous drones. These regulations are designed to ensure the safe operation of autonomous drones and mitigate potential risks. Here are some key aspects of the FAA's regulations regarding autonomous drones:Part 107 Regulations
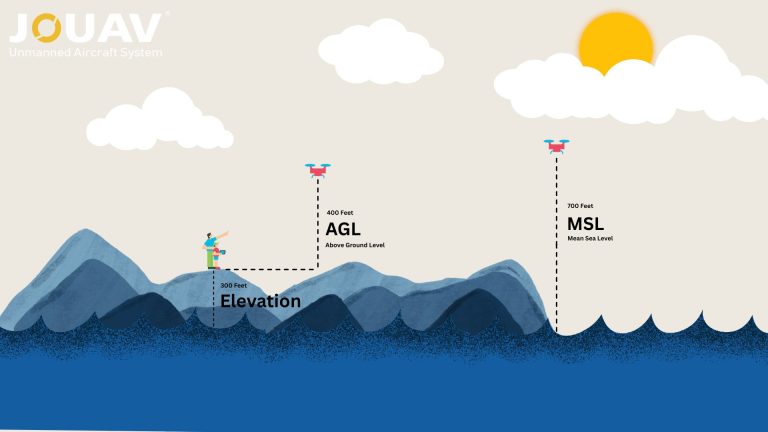
The FAA's Part 107 regulations apply to the operation of small unmanned aircraft systems (sUAS), including autonomous drones, for commercial purposes. These regulations require operators to obtain a Remote Pilot Certificate and follow specific rules, such as operating within visual line of sight (VLOS), not exceeding a maximum altitude of 400 feet above ground level, and maintaining a safe distance from people and property.Waivers for Beyond Visual Line of Sight (BVLOS) Operations
To conduct autonomous drone operations beyond visual line of sight (BVLOS), operators must obtain a waiver from the FAA. BVLOS operations involve using autonomous capabilities and relying on sensors, cameras, and other technologies to navigate and perform tasks without direct visual observation by the operator. The FAA carefully evaluates waiver requests to ensure safety and may require additional measures, such as the implementation of detect-and-avoid systems.Airspace Authorization and Restricted Areas
Autonomous drone operators must obtain airspace authorization from the FAA before operating in controlled airspace or near airports. This authorization ensures that drone operations do not interfere with manned aircraft operations. Additionally, certain areas, such as national security-sensitive locations or temporary flight restrictions (TFRs) due to events or emergencies, may have restricted drone access.Aircraft Certification and Compliance
Autonomous drone manufacturers must comply with FAA requirements for aircraft certification and registration. This includes meeting design and performance standards for safety, reliability, and airworthiness. Compliance with these standards ensures that autonomous drones are built and operated with the necessary safety measures in place.Remote Identification
The FAA has introduced a rule for remote identification of unmanned aircraft systems, including autonomous drones. This rule requires drones to broadcast identification information while in flight, allowing authorities and other stakeholders to identify and track the operation of drones. Remote identification helps promote accountability and addresses concerns related to security and privacy.How to Build an Autonomous Drone?
Building an autonomous drone requires a combination of hardware and software components. Here are some general steps involved in building an autonomous drone:
Step 1: Select or build the drone frame. Choose a suitable drone frame that meets your requirements for payload capacity, flight time, stability, and maneuverability.
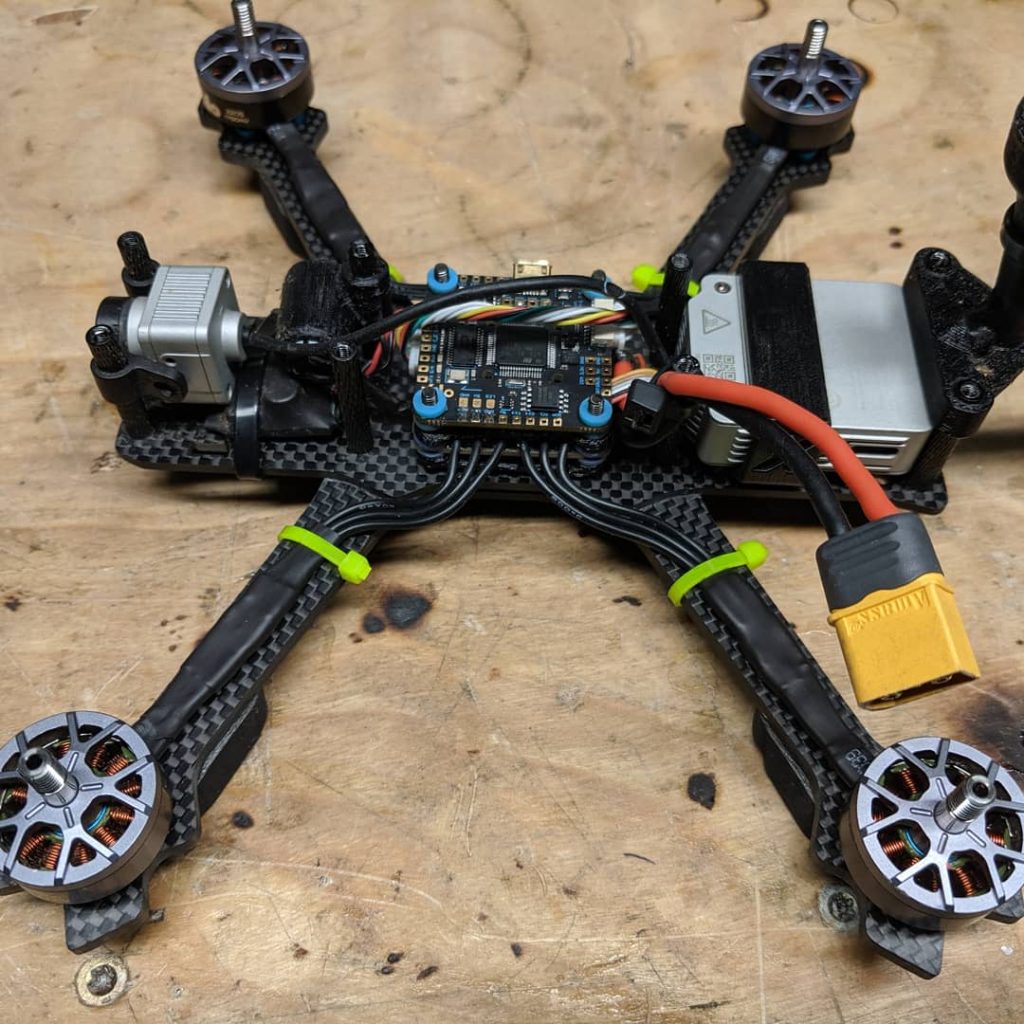

Step 2: Install the flight control system. Use a flight controller board, such as the popular ArduPilot or Pixhawk, to control the drone's flight movements and stability.
Step 3: Integrate various sensors like GPS, accelerometers, gyroscopes, and altimeters to gather data about the drone's position, orientation, and surroundings.
Step 4: Develop autonomous software. Write or use existing software algorithms to process sensor data, plan flight paths, and control the drone's actions autonomously.
Step 5: Implement communication and control. Establish a communication system to send commands to the drone and receive telemetry data in real-time. This can be done using radio transmitters/receivers or wireless protocols like Wi-Fi or cellular networks.
Step 6: Conduct thorough testing and iterations to refine the drone's autonomous capabilities, ensuring safety, reliability, and desired performance.
Building an autonomous drone can be a complex task, requiring knowledge in areas such as electronics, programming, and aeronautics. It's recommended to consult relevant resources, and tutorials, and possibly seek the guidance of experts to ensure a successful build.
FAQ
What is the Difference Between Autonomous and Automatic UAVs?
While the terms "autonomous" and "automatic" are often used interchangeably, there are subtle differences between the two concepts. The main difference between autonomous and automatic unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) lies in their level of independence and decision-making capabilities.
Autonomous drones have the ability to perceive their surroundings, make decisions, and execute tasks based on pre-programmed instructions or real-time data analysis. They possess a high degree of autonomy and can adapt to changing conditions, navigate complex environments, and complete missions with minimal human intervention.
Automatic UAVs, on the other hand, are designed to execute pre-defined tasks or follow predetermined flight paths without requiring real-time decision-making capabilities. These drones typically operate on a set of programmed instructions and perform repetitive tasks with a predefined sequence of actions.
How Much is the Autonomous Drone-In-A-Box?
The cost of an autonomous drone-in-a-box system can vary widely depending on several factors such as the brand, model, features, capabilities, and additional accessories or services included. Prices can range from a few thousand dollars to tens of thousands of dollars or more.
Can Drones be Automated?
Yes, drones can be automated. Automation refers to the ability of a drone to perform tasks or operate with minimal human intervention. Through the use of advanced flight control systems, sensors, and software algorithms, drones can execute predefined flight plans, follow waypoints, perform specific maneuvers, and even carry out complex missions. Automation allows drones to perform tasks efficiently, accurately, and autonomously, reducing the need for constant manual control.