Agriculture Drones | Farming Drones for Crop Monitoring
The agriculture drone market is booming, with a valuation of $4.17 billion in 2022 and a projected growth of $18.22 billion by 2030, boasting a 20.3% compound annual growth rate (CAGR).
Drones have found diverse applications on farms of all scales, from field scouting to enhancing security measures. The data they collect isn’t just numbers; it’s the backbone of 'precision agriculture,' guiding farmers towards informed decisions that can boost yields by up to 5%, a game-changer in an industry known for tight profit margins.
In this article, we'll explore agriculture drones' current and emerging applications and provide insights into the best drone options for agricultural use.
First, let's delve into the advantages of agricultural drones. In this section, we'll uncover the numerous benefits these unmanned aerial vehicles bring to farming, ranging from precise farming practices to cost-effectiveness.
Understanding the practical applications of drones in agriculture is essential. Here, we delve into the diverse roles that drones play in modern farming, from crop monitoring and mapping to livestock management and environmental conservation.
Precision Mapping and Surveying
Agriculture drones are outfitted with cutting-edge sensors and high-resolution cameras, facilitating precision mapping and surveying of agricultural landscapes. These technological marvels empower farmers with intricate insights into topographical variations, soil composition, and drainage patterns across their fields. The resulting data serves as the foundation for optimized planting strategies, resource allocation, and land management.
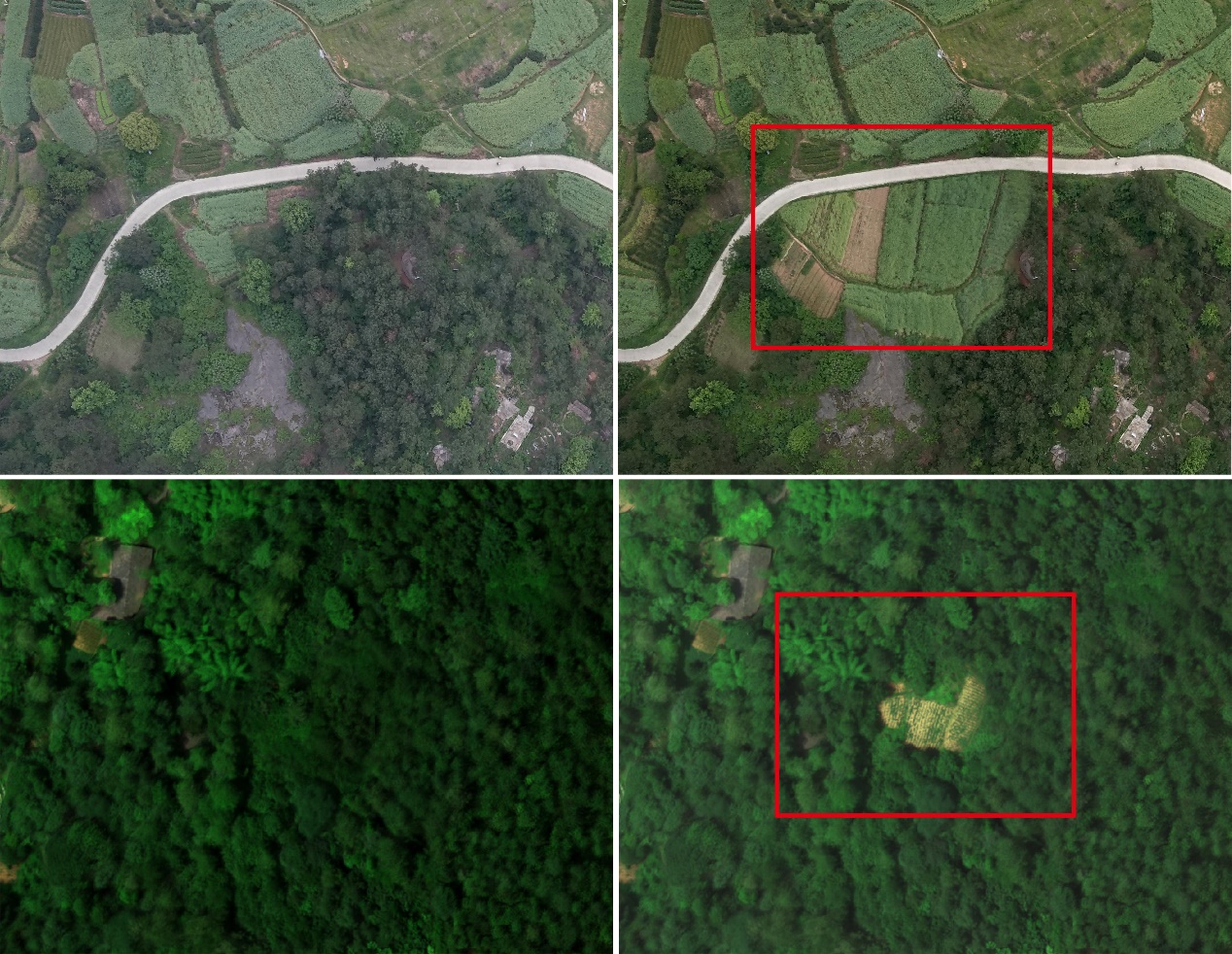

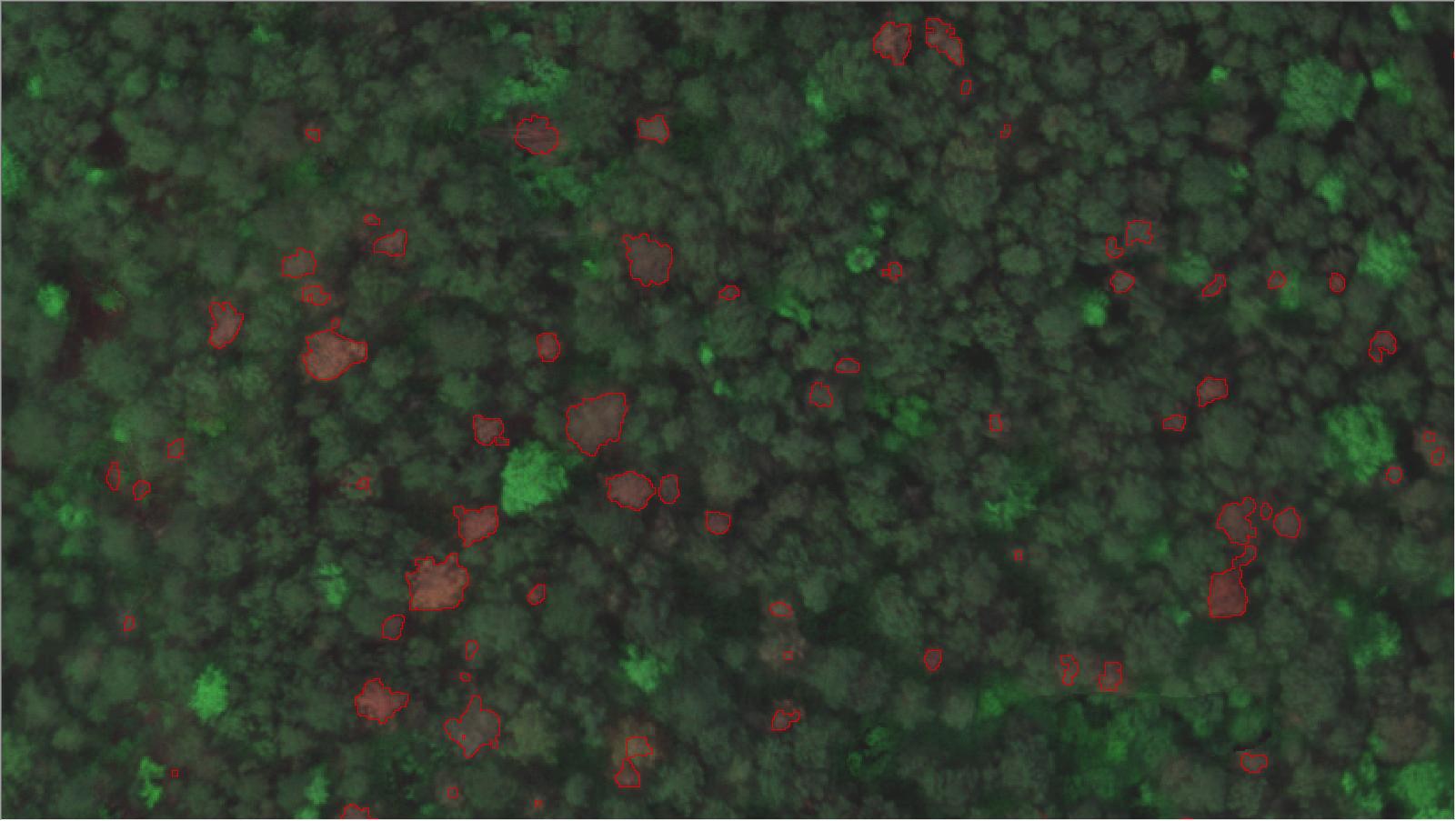
Vigilant Plant Health Monitoring
Agricultural drones, equipped with advanced multispectral and infrared cameras, excel in plant health assessment. By discerning subtle variations indicating stress, nutrient deficiencies, or diseases, professionals can implement precise remedial actions. Proactive measures translate into higher-quality crops and sustainable agricultural ecosystems.
Comprehensive Soil Health Analysis
Soil health forms the bedrock of productive agriculture. Drones facilitate the collection of diverse soil samples across fields. Through meticulous analysis, agricultural professionals gain insights into soil fertility, pH levels, and moisture content. Informed decisions regarding nutrient management, waterlogging, and soil conditioning enhance agricultural productivity and longevity.
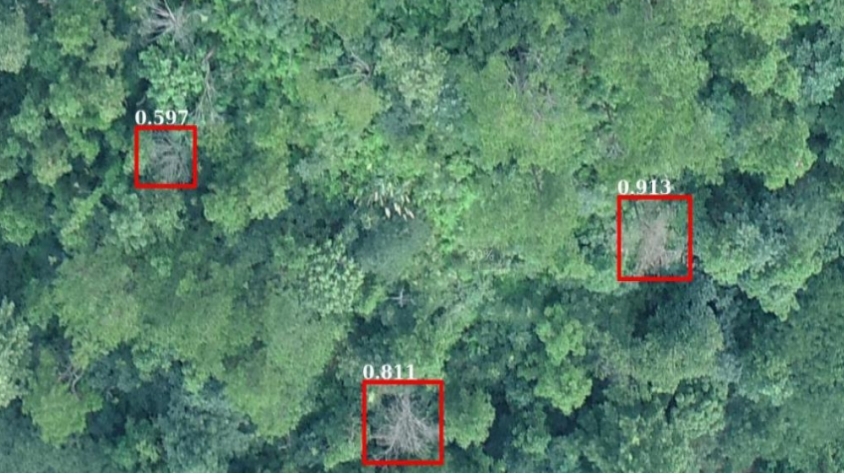
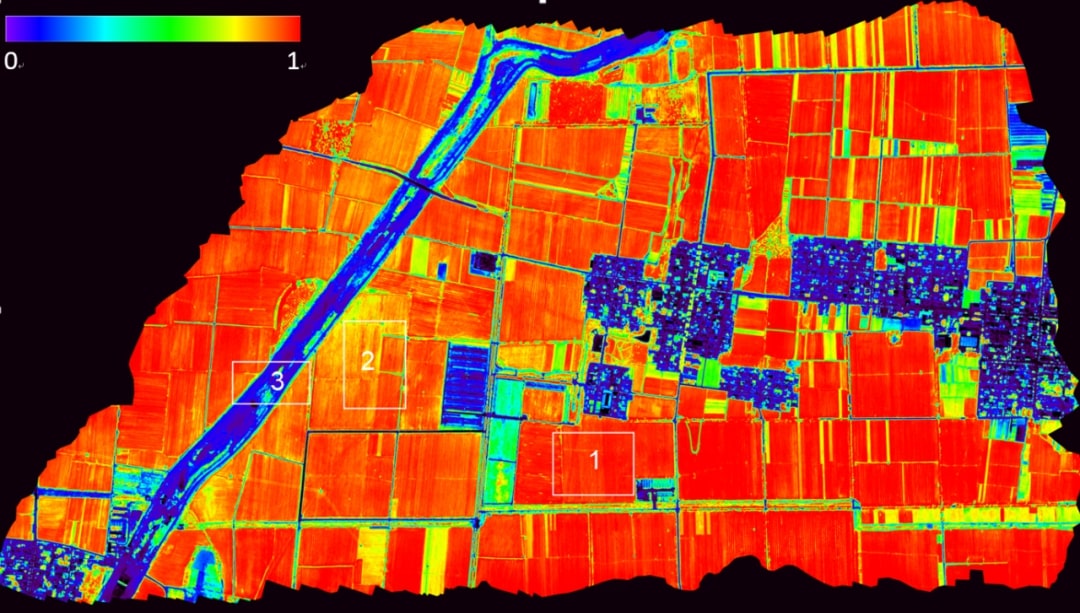

Real-Time Aerial Surveillance and Field Monitoring
Drones provide an unparalleled vantage point, facilitating real-time aerial surveillance of agricultural landscapes. Through continuous monitoring, professionals can promptly identify challenges such as water stagnation, pest infestations, or crop diseases. Timely intervention, based on these observations, mitigates risks and ensures optimal crop health, thereby safeguarding yields and farm profitability.
Livestock Management and Health Assessment
Beyond crop-centric applications, drones play a pivotal role in livestock management. Professionals utilize drones to monitor livestock health, track animal movements, and assess pasture conditions. This holistic approach to agriculture ensures the well-being of both crops and livestock, fostering integrated farming practices.
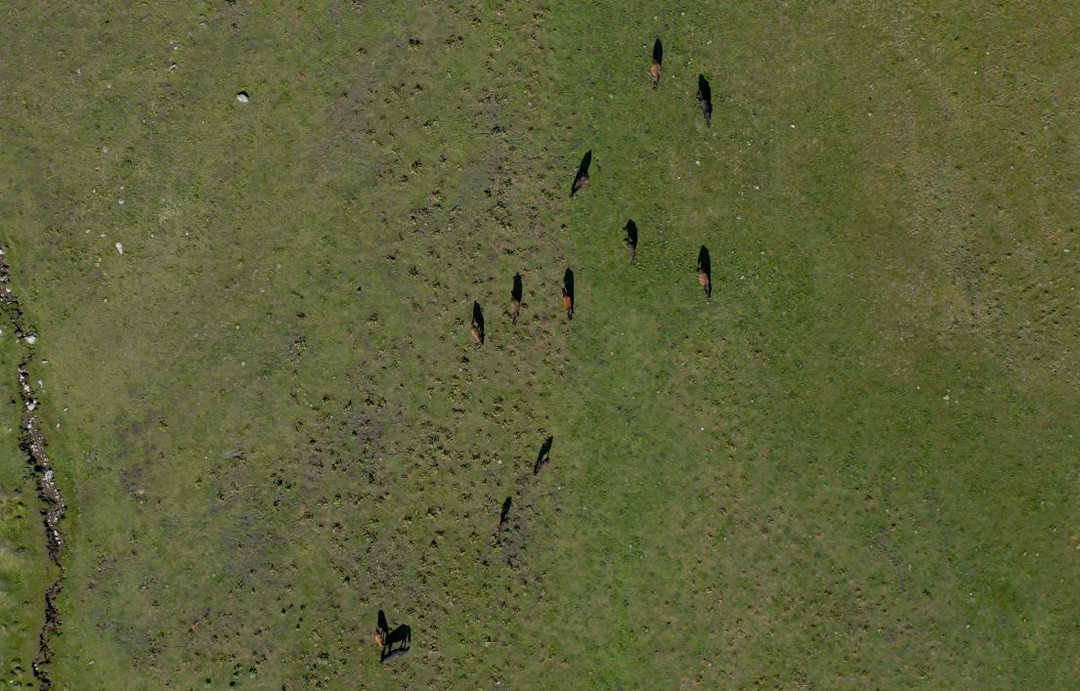

Using high-resolution RGB cameras and professional multispectral sensors on drones like JOUAV drones can indeed provide valuable insights into crop health and help in early detection and quantification of crop health problems.
Understanding the practical applications of drones in agriculture is essential. Here, we delve into the diverse roles that drones play in modern farming, from crop monitoring and mapping to livestock management and environmental conservation.

VTOL Capability for Terrain Challenges
JOUAV drones are equipped with Vertical Takeoff and Landing (VTOL) capability, overcoming challenges posed by large fields, difficult terrains, and steep landscapes. Unlike conventional drones, JOUAV drones do not require smooth surfaces for take-off and landing, ensuring adaptability to diverse agricultural environments.
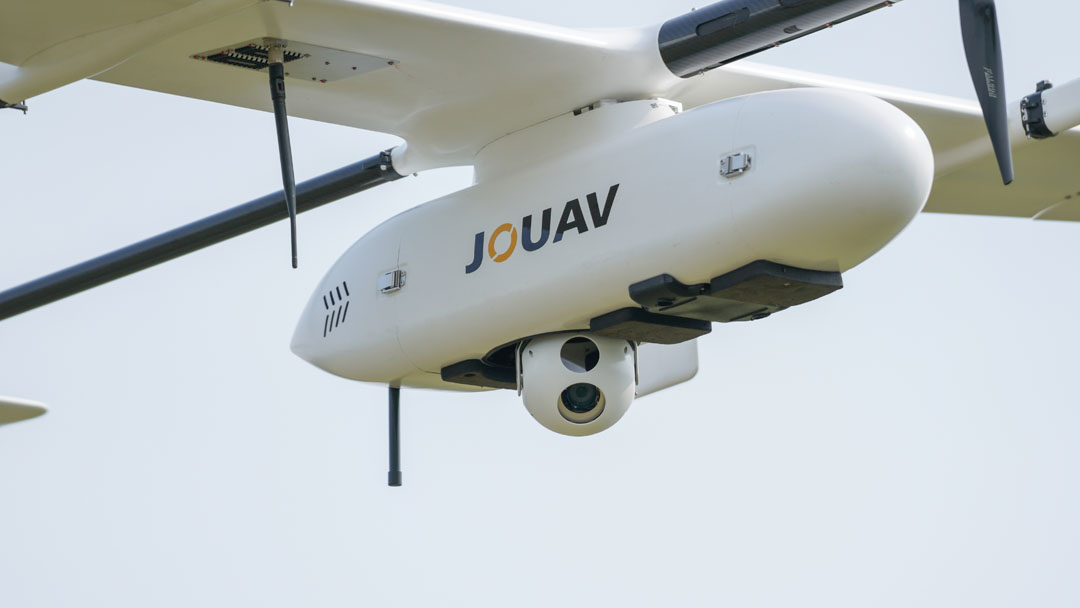

Versatile Payloads for Varied Applications
With an impressive 8kg payload capacity, JOUAV drones offer versatility in applications. They can be equipped with a range of sensors including a 1845m long-range LiDAR sensor, a 61MP RGB camera, and a multispectral camera featuring 6 multispectral sensors with 1.2MP. This flexibility enables precise data collection tailored to different agricultural needs.
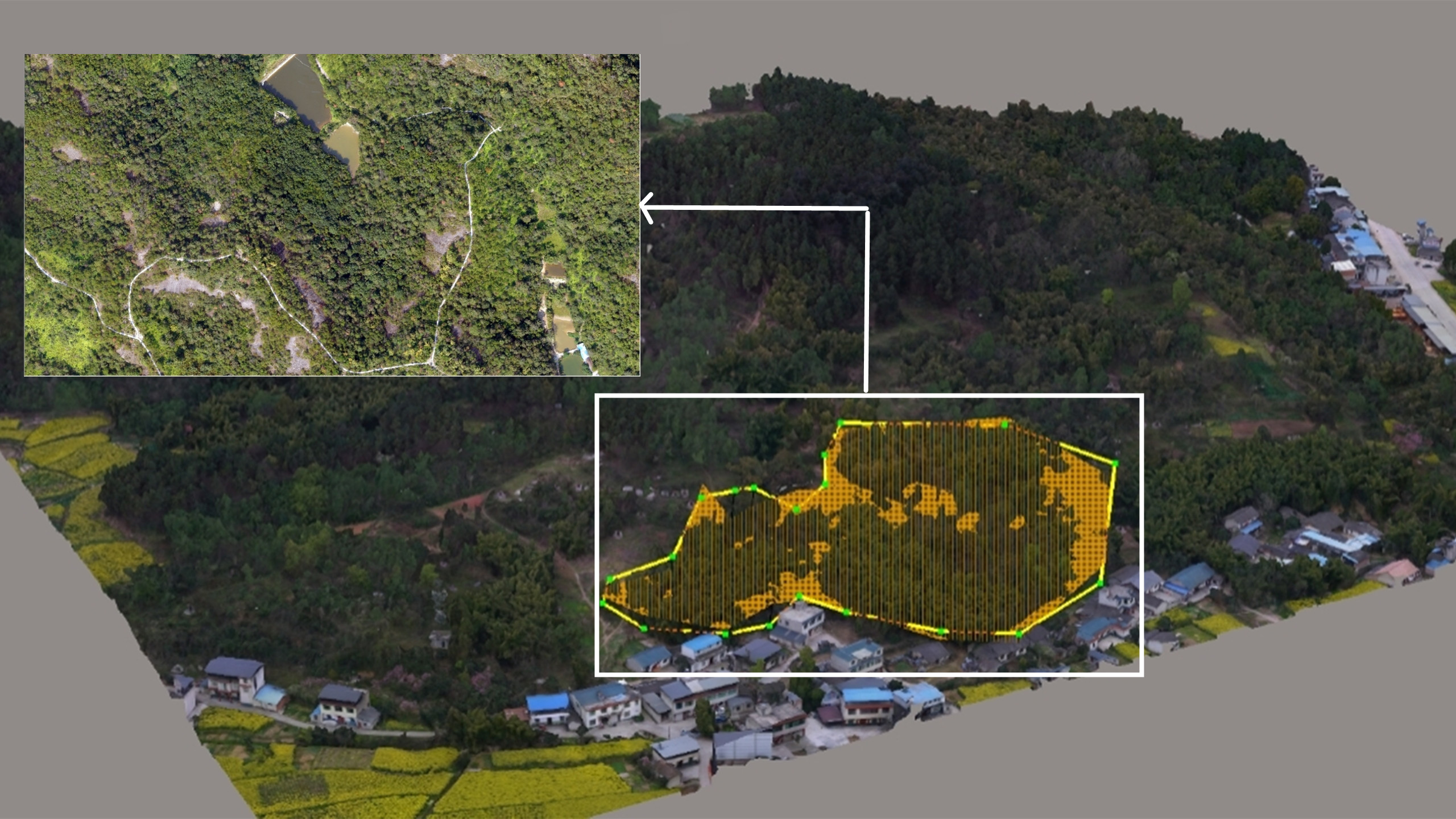
High-Resolution Data for Advanced Research
For agricultural researchers and agronomists focused on cutting-edge vegetation research, JOUAV drones furnish high-resolution data. These drones can achieve a staggering 1.2cm (0.47in) full-color sharpened ground resolution at an altitude of 60m (200ft). This extraordinary level of detail empowers precise data collection, facilitating meticulous vegetation analysis and research pursuits.

Exceptional Efficiency in Flight
JOUAV drones excel in efficiency, offering long flight times of up to 480 minutes and a cruising speed of 90km/h, with an impressive 200km long-range capability. The efficiency of these drones is particularly notable when compared to multi-rotor drones. A single flight of the JOUAV CW-15 can cover the same area as 14 flights of a multi-rotor drone. This efficiency translates to significant time and resource savings for farmers.

Autonomous Flight Capabilities
JOUAV drones elevate the standards of safety and ease of operation with their autonomous flight capabilities. These drones possess the intrinsic capacity to autonomously circumvent obstacles during flight and return independently in the event of operational anomalies, thus reducing the risk of accidents and simplifying operational control.
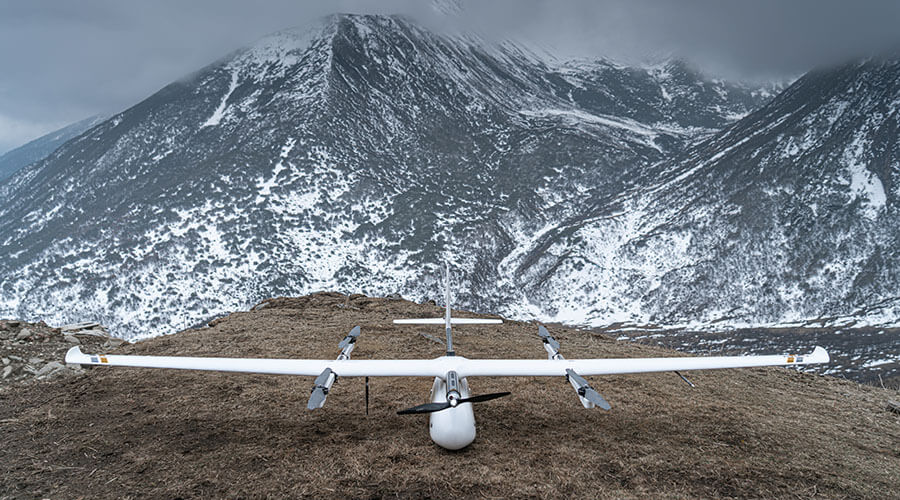

Superior Performance in Extreme Weather
JOUAV drones excel in extreme weather, ensuring reliable operation in high altitudes, humidity, low temperatures, and light rain. They feature power optimization and innovations like heated airspeed tubes and waterproofing, making them ideal for farms in diverse weather conditions.
Sometimes, seeing is believing. Let's dive into real-world stories of farmers who've harnessed the power of JOUAV drones to revolutionize their crops.
What Are the Different Types of Agricultural Drones?
Agriculture drones come in various forms, each tailored to specific agricultural applications. Understanding the advantages and disadvantages of these drone types is crucial for optimizing their utility in farming practices.
Fixed-Wing Drones
Fixed-wing drones are well-suited for large-scale farming operations. They efficiently cover extensive areas in a single flight, making them ideal for surveying vast farmlands. Their longer flight times compared to multirotor drones enable them to complete more comprehensive mapping and surveying tasks before needing to recharge or replace batteries. Moreover, due to their aerodynamic design, fixed-wing drones tend to handle windy conditions better, ensuring consistent data collection even in adverse weather.
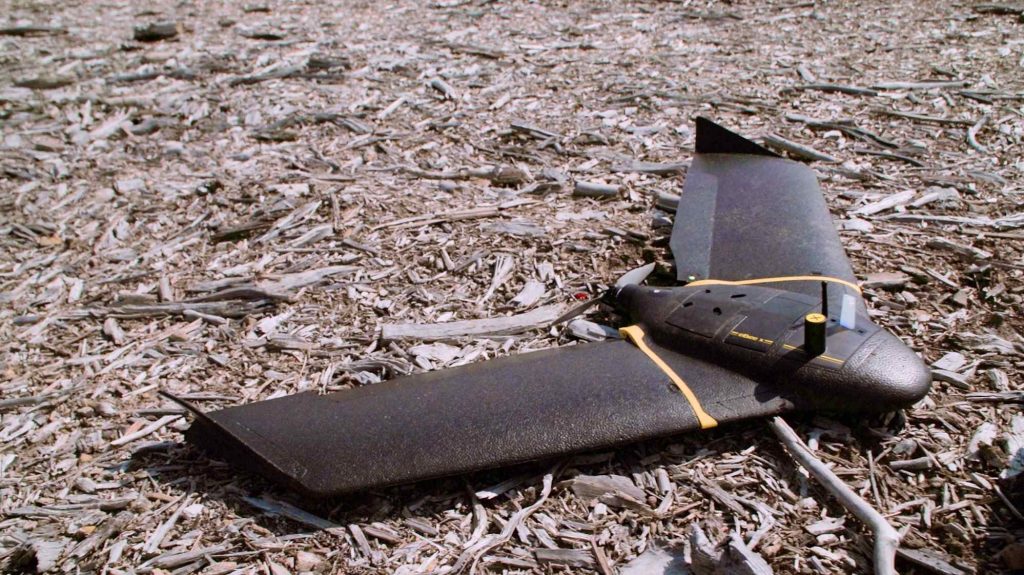

However, fixed-wing drones have limited maneuverability compared to multirotor drones. They cannot hover or make quick changes in direction, which may be a drawback when precise positioning is required. Additionally, takeoff and landing can be more challenging, as they require a runway-like space. The higher initial cost of fixed-wing drones might also be a consideration for smaller farms or operations with budget constraints.
Multirotor Drones
Multirotor drones, such as quadcopters and hexacopters, excel in maneuverability. They can hover, change direction rapidly, and fly at low altitudes, making them ideal for close inspection of crops and precise applications. These drones are typically easier to operate and require less training than fixed-wing drones, allowing farmers to quickly integrate them into their daily operations. Their vertical takeoff and landing capability eliminates the need for a runway or open space.

Multirotor drones generally have shorter flight times compared to fixed-wing and VTOL drones, which may necessitate frequent battery changes or recharging during longer tasks. Additionally, due to their shorter flight times and lower speed, multirotor drones are better suited for smaller to medium-sized fields, as covering extensive areas may require multiple flights and battery swaps.
VTOL (Vertical Takeoff and Landing) Drones
VTOL drones combine the advantages of both fixed-wing and multirotor drones. They can take off and land vertically like multi-rotors and transition to fixed-wing flight for efficient long-distance coverage. This versatility makes them suitable for farms with varied topography, as they can navigate rugged terrain and conduct aerial surveys over large areas. They also offer extended flight times compared to pure multirotor drones.
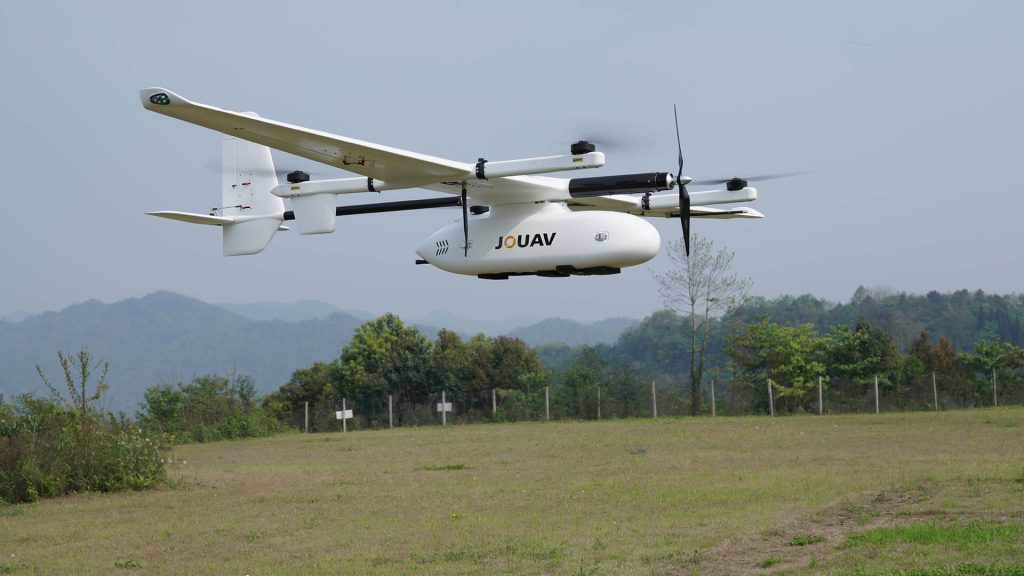

VTOL drones can be more complex to operate and maintain compared to standard multirotors, requiring proper training and expertise. Additionally, they tend to be more expensive due to their hybrid design and advanced capabilities, which may be a consideration for budget-conscious farmers.
What Are the Components of Agriculture Drone?
To comprehend the capabilities of agriculture drones, it's essential to understand their core components. This section breaks down the key elements that make these drones effective tools for modern farming.
Frame
The frame of an agriculture drone serves as its structural backbone. It is typically made from lightweight materials such as carbon fiber or aluminum to keep the drone agile and aerodynamic while ensuring durability. The frame houses all the other components and provides the necessary structure for mounting the motors, propellers, and other hardware.
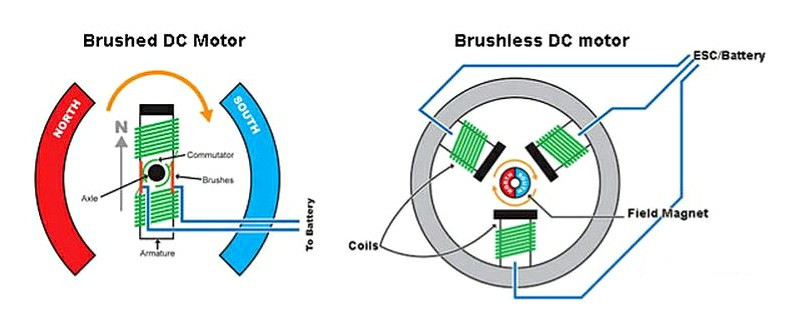
Motors
Motors are the powerhouse of agriculture drones. These electric motors generate the necessary thrust to lift the drone off the ground and keep it airborne. Agriculture drones typically use brushless DC motors for their efficiency and reliability. The number and size of motors may vary depending on the drone's design and payload capacity.
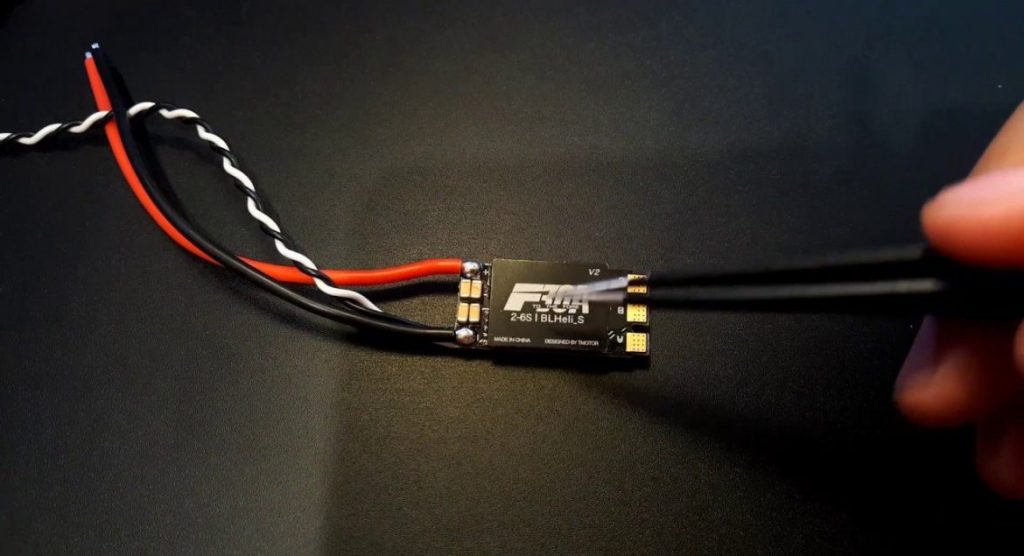
Electronic Speed Control (ESC)
Electronic Speed Control (ESC) for drones is a crucial electronic device that manages the speed and direction of each motor in the drone. It interprets signals from the flight controller, adjusting the power supplied to the motors to control their revolutions per minute (RPM) and, consequently, the drone's movement and stability during flight. In essence, it acts as a bridge between the flight controller and the motors, ensuring precise control and maneuverability of the drone.
Flight Control Board
The flight control board, often referred to as the "brain" of the drone, is responsible for processing data from various sensors and sending commands to the motors and ESCs. It plays a crucial role in stabilizing the drone, ensuring it stays level and responds to pilot inputs accurately. Flight control boards are equipped with advanced algorithms and sensors like accelerometers and gyroscopes to provide stability and precise control.
Radio Receiver
The radio receiver receives signals from the drone operator's transmitter, translating them into commands that the flight control board can execute. This component enables remote control of the drone, including functions such as throttle, pitch, roll, and yaw, allowing the pilot to navigate and control the drone's movements.
Propellers
Propellers are responsible for generating the thrust required to lift and propel the drone. Agriculture drones often use specially designed propellers optimized for efficiency and stability during aerial operations. Propeller size, pitch, and rotation direction are carefully selected to match the drone's design and intended use.

Battery
The battery is the primary source of power for the agriculture drone. Lithium-polymer (LiPo) batteries are commonly used due to their high energy density and lightweight properties. The capacity and voltage of the battery directly influence the drone's flight time and payload capacity. Advanced battery management systems ensure safe and efficient power delivery.
Gimbal
Agriculture drones are often equipped with gimbals to stabilize cameras and sensors mounted on board. A gimbal allows the camera or sensor to maintain a steady orientation, even when the drone experiences turbulence or changes in direction. This stability is crucial for capturing accurate and usable data during agricultural surveys and inspections.
Sensors
Sensors constitute the sensory array of agriculture drones, each tailored to specific functions:
- Cameras: Agriculture drones often have cameras capable of capturing high-resolution images and These cameras may include RGB (visible light), multispectral, or thermal imaging sensors.
- LiDAR(Light Detection and Ranging): LiDAR sensors use laser beams to create detailed 3D maps of the terrain, making them useful for terrain mapping and elevation
- InfraredSensors: Infrared sensors are used for monitoring crop health, identifying stress in plants, and detecting temperature
- UltrasonicSensors: Ultrasonic sensors help drones maintain a consistent altitude above the ground, especially during low-altitude
How Much Do Agricultural Drones and Services Cost?
Here, we'll dissect the costs associated with drone adoption, including drone prices, operating expenses, and service fees, to provide a comprehensive understanding of the economic factors at play.
How Much Does an Agriculture Drone Cost?
Agriculture drones span a wide price spectrum based on their features, capabilities, and intended applications:
- Entry-level drones: These drones, suitable for basic aerial photography and mapping, are typically priced in the range of $1,000 to $2,000. While they may lack advanced sensors, they serve as excellent starting points for small-scale
- Mid-range drones: More versatile and equipped with advanced sensors (such as RGB cameras and multispectral sensors), mid-range drones range from $2,000 to $10,000. These offer enhanced data collection capabilities, making them popular choices for mid-sized
- High-end drones: Tailored for precision agriculture, high-end drones can cost $10,000 to $200,000 or even come equipped with cutting-edge technology, including LiDAR sensors and thermal cameras, enabling comprehensive data collection and analysis.
How Much Does Drone Cost Per Acre?
Determining the cost of drone operation per acre requires a meticulous assessment of several factors:
- DroneModel: The initial investment in a drone, its maintenance costs, and depreciation over time contribute to the cost per
- OperationalCosts: Ongoing expenses such as battery replacements, fuel or electricity usage, and regular maintenance impact the
- Efficiency: Longer flight times and efficient operations can reduce the cost per acre, as they maximize the area covered within a single
- Payload and Sensors: Costs can vary depending on the type and quality of sensors and cameras used for data Specialized sensors, like LiDAR or thermal cameras, come at a higher cost.
While the cost per acre may fluctuate widely based on these factors, it typically ranges from $5 to $50 per acre. The exact cost depends on the specific tasks performed by the drone, the technology used, and the service provider's rates.
How Much Does an Agriculture Drone Cost Per Hour?
Evaluating the hourly cost of operating an agriculture drone involves accounting for multiple components:
- Fuel or Battery Usage: Calculating the cost of fuel or electricity required for drone operation during the specified time
- Maintenance: Ongoing maintenance expenses, including regular check-ups and potential parts
- PilotFees: If a certified drone pilot is required for operation, their hourly fees should be included in the
- Insurance: Costs associated with drone insurance to cover potential liabilities and damages
Hourly operating costs typically fall within the range of $20 to $100 or more, depending on the drone model, service type, and specific operational factors. This cost encompasses both direct expenses and any associated professional fees.
How Much Do Agriculture Drone Services Cost?
Agriculture drone services offer a wide array of options tailored to the specific needs of farmers and landowners. Costs for these services vary based on several factors, including the type of service, the area covered, data processing requirements, and the frequency of monitoring.
Here's a breakdown of approximate cost ranges for different agriculture drone services:
Aerial Mapping Services:
Basic Aerial Mapping: Typically costs between $300 and $1,000 per flight. This service captures high-resolution aerial imagery of fields for basic visual assessment.
Advanced Mapping with Data Analysis: Priced in the range of $1,000 to $3,000 per flight, this service includes data analysis and specialized data products like orthomosaic maps and digital elevation models (DEMs).
Crop Monitoring Services:
Basic Crop Monitoring: Ranges from $500 to $1,500 per flight. It includes capturing images for crop health assessment and may vary based on the area covered and monitoring frequency.
Advanced Monitoring with Data Analysis and Reporting: Costs between $1,500 and $5,000 per flight, offering in-depth crop monitoring with data analysis, including NDVI mapping, disease detection, and yield forecasting.
Pest Control and Precision Application Services:
Costs for pest control and precision application services range from $10 to $50 per acre. The exact cost depends on factors such as chemical type, area size, and complexity of the task.
Data Analysis and Reporting Services:
Typically priced between $200 and $500 per hour of analysis. Costs can vary based on the complexity of the analysis and the volume of data being processed. These services provide insights from drone-collected data.
Ongoing Monitoring Services (Seasonal or Annual Packages):
Annual monitoring packages vary widely, ranging from $5,000 to $20,000 or more. These packages often cover multiple flights throughout the growing season, comprehensive data analysis, and regular reporting.
FAQ
What is a Drone in Agriculture?
A drone in agriculture, often referred to as an agricultural drone or UAV (Unmanned Aerial Vehicle), is a specialized aircraft equipped with various sensors, cameras, and data collection tools. These drones are designed for use in farming and agricultural applications. They range from small quadcopters to larger fixed-wing aircraft and are used to monitor crops, livestock, and land, providing valuable data for precision agriculture.
How Many Acres Can a Drone Cover?
The coverage area of an agriculture drone depends on several factors, including its flight time, battery capacity, and the specific mission it's performing. On average, a drone can cover anywhere from 100 to 500 acres in a single flight, although advanced models with longer flight times can cover larger areas. Keep in mind that the speed of the drone, altitude, and camera specifications also influence coverage.
What is the Range of Agriculture Drone?
Spraying drones in agriculture typically have a range of 1 to 5 kilometers. Specialized mapping drones like JOUAV can cover extensive distances, reaching up to 200 kilometers or more. This extended range is crucial for large-scale mapping and surveying in agriculture.
How Much Does a Spray Drone Cost?
The cost of a spray drone varies widely based on its specifications and capabilities. Entry-level agricultural spray drones can start at around $5,000 to $10,000, while more advanced models equipped with higher payload capacities and precision technology can cost $15,000 or more.
The cost per hectare for drone spraying typically ranges from $10 to $20, depending on factors like the type of crop, the size of the area, the chemicals used, and the drone's efficiency. However, it's generally considered cost-effective due to reduced chemical usage and labor savings.
What are the Disadvantages of Drones in Farming?
While agricultural drones offer numerous advantages, they also have some disadvantages to consider. These include:
- Initial Investment: Drones and their equipment can be costly.
- Regulatory Challenges: Compliance with aviation and privacy regulations can be complex.
- Skill Requirements: Operating and maintaining drones require trained personnel.
- Data Management: Handling and interpreting the large amounts of data generated can be challenging.
- Technical Issues: Drones may experience technical malfunctions or crashes.
What is the Best Drone Software for Agriculture?
Choosing the best drone software for agriculture depends on your specific needs. Some popular options include:
- DroneDeploy: Offers mapping, analytics, and crop health monitoring.
- Pix4D: Known for its photogrammetry software for creating 2D and 3D maps.
- Agisoft Metashape: Used for creating high-quality geospatial data and 3D models.
- PrecisionHawk's DataMapper: Provides data analytics and insights for precision agriculture.
What is the Future of Agricultural Drones?
The future of agricultural drones is promising, with several trends expected:
- Advanced Technology: Continued advancements in battery life, autonomy, and sensor technology.
- Data Analytics: More sophisticated AI and machine learning for data analysis.
- Regulatory Changes: Evolving regulations to support expanded drone use in agriculture.
- Integration: Drones will become an integral part of precision agriculture, helping farmers make data-driven decisions for improved crop yields, resource efficiency, and sustainability.